Edward Kellman, CEO and chief design engineer of Trakker Apps, holds two U.S. patents for an innovative take on double-entry accounting
The system, known as the Double-Entry Multi-Extrinsic-Variable Accounting Method Database, aims to modernize financial tracking while preserving the essence of the traditional accounting system that was first described by Luca Pacioli back in 1494. It leverages artificial intelligence while generating and reconciling multiple financial ledgers by account, user, customer, job and vendor.
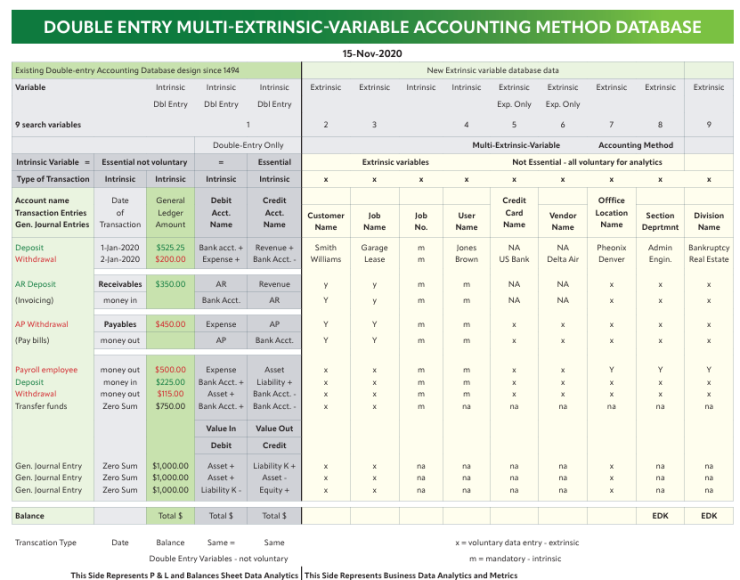
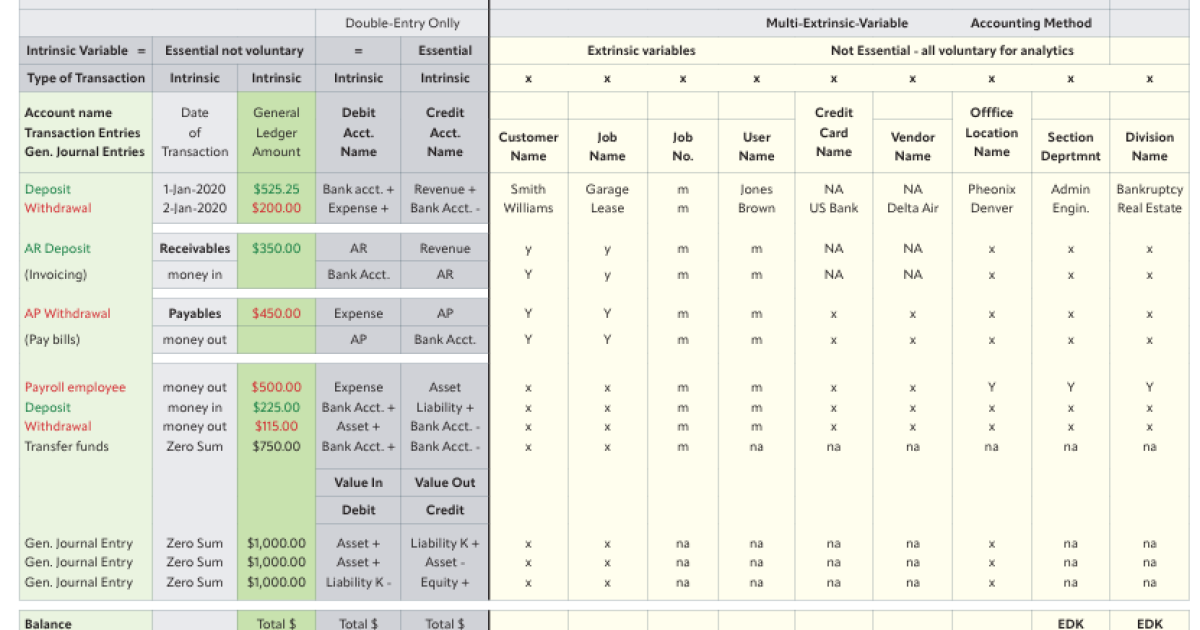
“I made a representation of the current double entry database, which basically collects a date, amount, a debit and a credit account, and that’s about as much of that calculation as you can do by hand,” said Kellman. “It’s been done by hand for hundreds of years. It’s very tedious, but nobody ever thought to expand the database now that you can use a computer to solve for these enormously complex database solutions.”
He expanded the database with new variables, which he calls extrinsic variables, and now it can track financial transactions by customer, job, user and vendor. “By doing that, I’ve created an enormous amount of new financial solutions that can be plucked from the database that never existed, and these are all financial analytics for your company, because the variables are the things that matter in your company: which jobs make the most money, which users produce the most income and expenses, and things of this nature,” said Kellman. “But because I expanded that database, and nobody thought to do this since 1494 when this system was first published. It’s totally modernized double entry accounting.”
He offers them as apps that can be downloaded from the Apple and Android app stores, along with a browser-based version through the Trakker Apps website. He is hoping to partner with financial institutions rather than accounting software companies since the system was developed as a BaaS, or banking-as-a-service, technology. The bank would be able to white label the program with its own branding.
The system leverages artificial intelligence to automate data entry. “I didn’t want it to become a tedious process for entering data, so we basically wrote these AI data entry algorithms that collect the data and fill in the data when it knows it right away,” said Kellman. “You can enter these transactions really just as quickly, if not quicker, on a smartphone than you can on any other accounting system, because of the data entry algorithms that just collect the data really quickly. And once you hit Enter and record that transaction, that’s all stored in the cloud. All your business is digitized.”
He did beta testing for a year on the app stores, where the program had around 6,000 downloads. But then he shut down the program because he didn’t want to be the cloud host responsible for storing thousands of people’s financial data so he is searching for a banking partner to host it securely. The system provides a kind of ERP platform that combines banking and accounting.
“Instead of printing profit and loss reports and balance sheet reports and trial balance summary reports just for the whole company, I can print them individually, for each individual user or each individual job,” said Kellman. “Or if you have multiple users, like in a law firm on one job, you can select the job and the user and print just the transactions that apply to those variables that you’ve selected, and now you’ve got a wealth of information about your company that never existed before.”
Trakker Apps’ BaaS fintech platform includes Business Trakker, Invoice 4 Business, Expense Trakker, Balance Sheet Trakker and Escrow Trakker for Lawyers.
It took four years before Kellman was able to patent the technology. “Normally, when you apply for a patent, they spend a lot of time on a patent search, where they investigate all the previous patents to see if you’re in violation of any other patents, or any other art that exists,” he said. “My patents are the only patents ever issued for a double entry accounting system, and there was no prior art. It took about four years to get it, and then I got a second one after that.”
Kellman isn’t planning to challenge other accounting software companies now that he has the patents, which are actually for the ledger. “No, I don’t want to challenge other companies,” he said. “You can’t patent a software program. My program produces what we call a multivariable ledger that you can hold in your hand. It’s a financial ledger, and that’s what’s patented.”

 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Finance1 week ago
Finance1 week ago
 Economics5 days ago
Economics5 days ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Blog Post6 days ago
Blog Post6 days ago
 Personal Finance5 days ago
Personal Finance5 days ago
 Personal Finance6 days ago
Personal Finance6 days ago