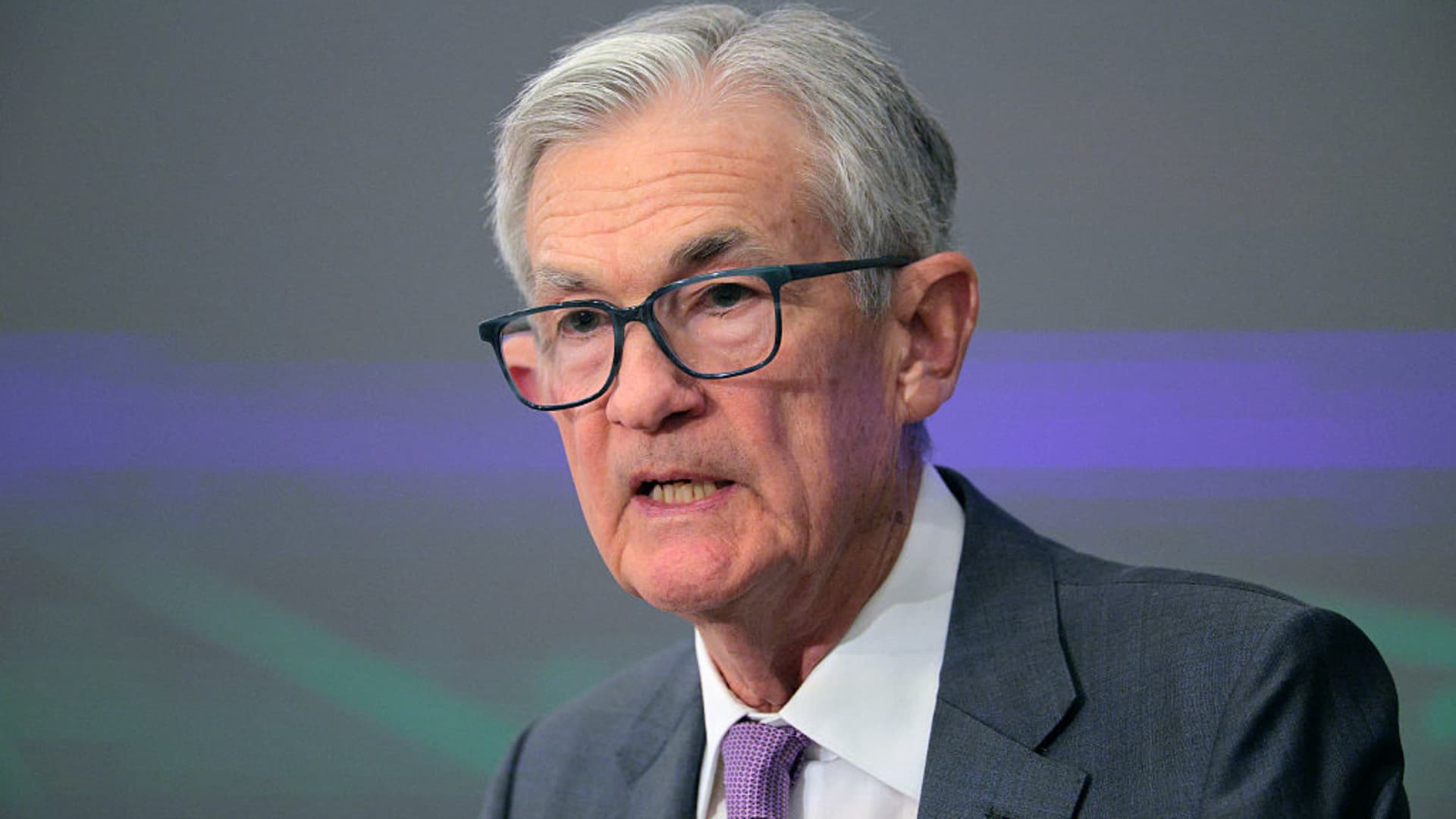
Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell delivers remarks during the Division of International Finance 7th Anniversary Conference at the Fed on June 02, 2025 in Washington, DC.
Chip Somodevilla | Getty Images
Federal Reserve officials get to voice their outlook this week on the future path of interest rates along with the impact that tariffs and Middle East turmoil will have on the economy.
While any immediate movement on interest rates seems improbable, the policy meeting, which concludes Wednesday, will feature important signals that still could move markets.
Among the biggest things to watch will be whether Federal Open Market Committee members stick with their previous forecast of two rate cuts this year, how they see inflation trending, and any reaction from Chair Jerome Powell to what has become a concerted White House campaign for easier monetary policy.
“The Fed’s main message at the June meeting will be that it remains comfortably in wait-and-see mode,” Bank of America economist Aditya Bhave said in a note. BofA thinks the Fed won’t cut at all this year but will leave open the possibility for one reduction. “Investors should focus on Powell’s take on the softening labor data, the recent benign inflation prints and the risks of persistent tariff-driven inflation.”
The committee’s “dot plot” grid of individual members’ rate expectations will be front and center for investors.
At the last update in March, the committee indicated the equivalent of two quarter percentage point reductions this year, which is in line with current market pricing. However, that was a close call, and just two participants changing their approach would swing the median forecast down to one cut.
The meeting comes against a complicated geopolitical backdrop in which the impact of President Donald Trump’s tariffs on inflation has been minimal so far but unclear for the future. At the same time, Trump and other administration officials have stepped up their urging of the Fed to lower rates.
On top of that, the Israel-Iran conflict threatens to destabilize the global energy picture, providing yet another variable through which to navigate policy.
“We expect Chair Powell to repeat his message from the May press conference,” Bhave said. “Policy is in a good place and there is no hurry for the Fed to act.”
However, the landscape could change quickly.
Varying economic signals
While the unemployment rate remains low at 4.2%, the May nonfarm payrolls report showed a continuing if gradual softening in the labor market. The most recent inflation data also indicated that tariffs have done little to impact prices at least on a macro scale, adding another incentive for the Fed to at least think about easing.
“We’re in a disinflating world,” former Dallas Fed President Robert Kaplan said in a CNBC interview last week. “If it weren’t for these prospective tariffs that will flow through and are flowing through, I think the Fed would be on their front foot looking to cut rates.”
As things stand heading into the meeting, markets are pricing in the next cut to come in September, which would be the one-year anniversary of a surprisingly aggressive half percentage point reduction the FOMC instituted amid concerns over the labor market. The committee added two more quarter-point moves by the end of the year and has been on hold since.
In the current climate, “trade tensions have diminished somewhat, inflation has been low, and the hard data have shown only limited signs of softening,” Goldman Sachs economist David Mericle wrote.
Goldman sees the Fed sticking with its two-cut forecast but the firm’s economists expect ultimately to see only one.
“We are confident that we are still on track for eventual rate cuts because aside from the tariffs, the inflation news has actually been fairly soft. While an earlier cut is possible, the peak summer tariff effects on the monthly inflation prints will most likely be too fresh for the FOMC to cut before December,” Mericle said.
Officials also will update their projections for employment, inflation and gross domestic product growth.
Goldman sees the FOMC taking up the inflation expectation to 3% for all of 2024, 0.2 percentage point higher than March. The firm also sees a slight lowering of GDP growth to 1.5% from 1.7% and a tick higher in the unemployment rate to 4.5%.
Officials will then use the summer to watch the data and judge from there what it will do later in the year, said Krishna Guha, head of global policy and central bank strategy at Evercore ISI.
“We think the FOMC will maintain its wait-and-see posture at its June meeting Wednesday, underline it still expects to learn a lot more about the evolving outlook over the next several months, and continue to point to September as the next decision point on rates,” Guha said in a note.

 Accounting1 week ago
Accounting1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Finance1 week ago
Finance1 week ago
 Finance7 days ago
Finance7 days ago