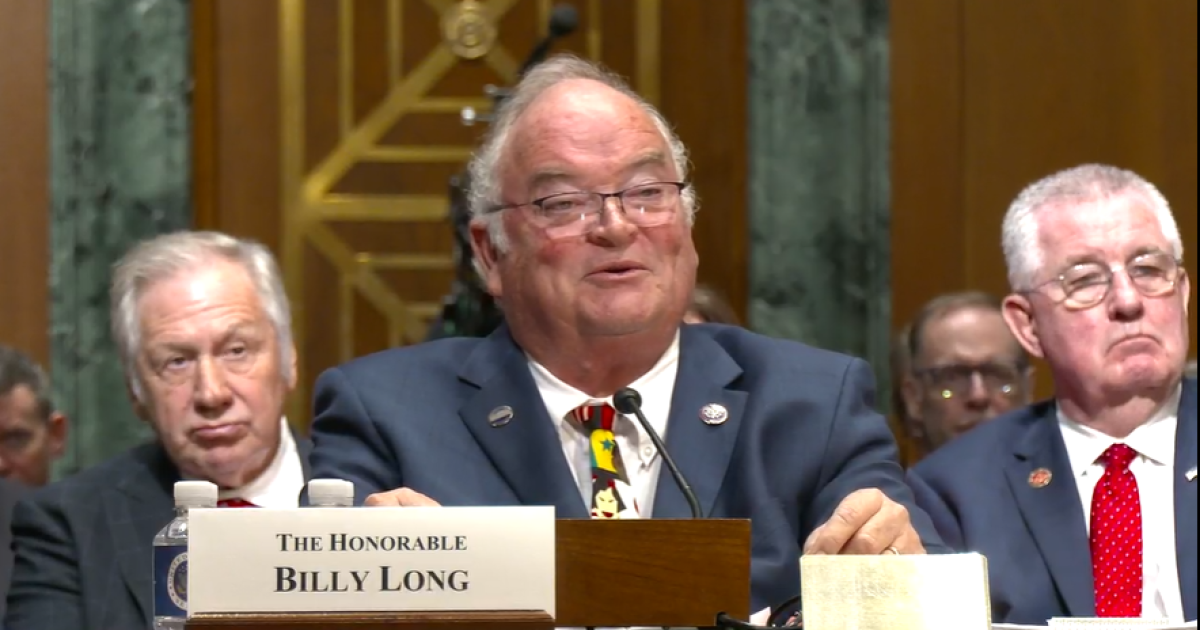
The Senate Finance Committee questioned Billy Young, President Trump’s nominee for Internal Revenue Service commissioner, about his plans for the beleaguered agency and promotion of dubious “tribal tax credits” and Employee Retention Tax Credits during a long-awaited confirmation hearing Tuesday after a series of acting commissioners temporarily held the role.
Trump announced in December he planned to name Long, a former Republican congressman from Missouri, as the next IRS commissioner, even though then-commissioner Danny Werfel’s term wasn’t scheduled to end until November 2027. Since then, the role has been filled by four acting commissioners who have faced pressures to accept drastic staff cuts at the agency and share taxpayer data with immigration authorities.
Long insisted during the confirmation hearing that he would defend the integrity of the IRS and maintain an open door policy, emulating the example of former commissioner Charles Rossotti, who served from 1997 to 2002.
“If confirmed, I will implement a comprehensive plan aimed at enhancing the IRS, but also one that develops a new culture at the agency,” he said in his opening statement. “I am eager to implement the necessary changes to maximize our effectiveness, while also remaining transparent with both Congress and taxpayers. It is important to also recognize the dedicated professionals currently at the IRS whose hard work too often goes unnoticed. It is my pledge that we will invest in retaining skilled members of the team. This does not mean a bloated agency, but an efficient one where employees have the tools they need to succeed.”
Committee chairman Mike Crapo, R-Idaho, expects to see changes at the agency. “Congressman Long is very clear that he will make himself available to all IRS employees, no matter their seniority,” Crapo said in his opening statement. “Moreover, he wants to implement a top-down culture change at the agency. This sea change will benefit American taxpayers, who too often view the IRS as foe, rather than friend. Congressman Long knows, from years of experience in the House, that to be a successful Commissioner, he must be a valuable partner in Congress’ efforts to ensure that new tax legislation is implemented and administered as Congress intends it to be. I am also confident that he will be fully transparent and responsive to Congress and the American people.”
Sen. Ron Wyden, D-Oregon, the top Democrat on the committee, questioned Long about his promotion of “tribal tax credits” and the fraud-plagued ERTC. “Most of Congressman Long’s experience with tax issues came after he left Congress, when he dove headlong into the tax scam industry,” he said in his opening statement. “Cashing in on the credibility of his election certificates, he raked in referral fees steering clients to firms that sold faked tax shelters and pushing small businesses to unknowingly commit tax fraud.”
Wyden asked Long about the $65,000 he earned from referring friends to tax promoters who claimed they had acquired income tax credits issued to a Native American tribe and then sold the tax credits to investors. “There’s a problem. The IRS said in March that the credits do not exist. They’re fake. They are a scam. Now you’re asking to be put in charge of the IRS, and the IRS confirms that these aren’t real. Tell the committee, do you believe these so-called tribal tax credits actually exist?”
Long insisted his only involvement with the credit was to connect interested friends and offer to put them on a Zoom call with someone, but he was not on the Zoom calls himself. Wyden pressed him on whether the tax credits actually exist.
“I think the jury’s still out on that,” Long admitted. “I know since 2022 they’ve been accepting them, so now they claim that they’re not. I think that all this is going to play out, and I want to have it investigated, just as you do. I know you’re very interested in this subject. I am too.”
Wyden also asked about $165,000 in campaign donations that went to Long’s unsuccessful 2022 Senate campaign after Trump named him as the next IRS commissioner. Long insisted he had followed guidelines from the Federal Election Commission. “You know as well as I do, anytime you’re dealing with the FEC, you have to follow FEC guidelines, and that’s exactly what I did all the way,” he said.
Wyden then asked him about his work with promoters of the Employee Retention Tax Credit. “You stated on a YouTube video that everybody qualifies for the Employee Retention Tax Credit, and you urge listeners to ignore CPAs that said they didn’t qualify. Do you really think everybody qualifies?”
“If you listen to that video, I hate to correct you, but I didn’t say everyone qualifies,” Long responded. “I said virtually everyone qualifies, meaning most people.”
Sen. Elizabeth Warren, D-Massachusetts, and other Democrats also questioned Long about whether he would follow Trump’s orders to audit certain taxpayers or remove the tax-exempt status of organizations, even if it violated the law. Long insisted he would follow the law but declined to explicitly say whether he would defy an order from Trump.
“I don’t intend to let anybody direct me to start an audit for political reasons,” he said.


 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Personal Finance7 days ago
Personal Finance7 days ago
 Economics6 days ago
Economics6 days ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics5 days ago
Economics5 days ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago