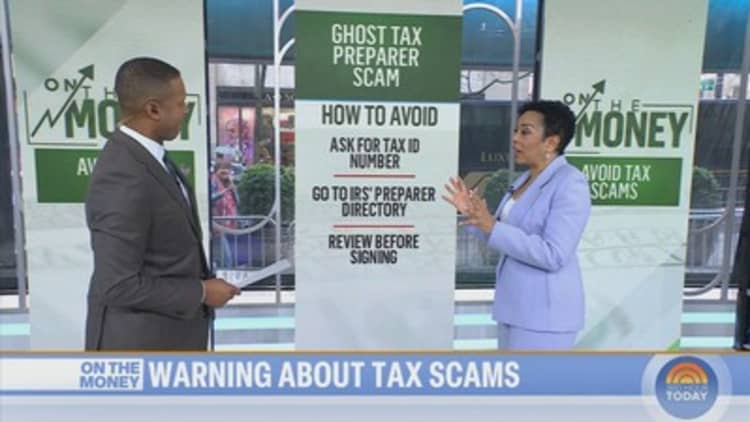
Brendon Thorne | Bloomberg | Getty Images
Some Americans believe real estate and gold are the best long-term investments. Advisors think that’s misguided.
About 37% of surveyed U.S. adults view real estate as the best investment for the long haul, according to a new report by Gallup, a global analytics and advisory firm. That figure is roughly unchanged from 36% last year.
Gold was the second-most-popular choice, with 23% of surveyed respondents. That’s five points higher than last year.
To compare, just 16% put their faith in stocks or mutual funds as the best long-term investment — a decline of six percentage points from 2024’s report, Gallup found.
The firm polled 1,006 adults in early April.
Here’s a look at other stories impacting the financial advisor business.
Financial advisors caution that this preference is likely more about buzz than fundamentals. Be careful about getting caught up in the hype, said certified financial planner Lee Baker, the founder, owner and president of Claris Financial Advisors in Atlanta.
Carolyn McClanahan, a CFP and founder of Life Planning Partners in Jacksonville, Florida, agreed: “People are always chasing what’s hot, and that’s the stupidest thing you could do.”
Here’s what investors need to know about gold and real estate, and how to incorporate them in your portfolio.
Why gold and real estate are alluring
Baker understands why people like the idea of real estate and gold: Both are tangible objects versus stocks.
“You buy a house, you can see it, feel it, touch it. Your investment in stocks perhaps doesn’t feel real,” said Baker, a member of CNBC’s Financial Advisor Council.
While the preference for gold grew this year, the share of Gallup respondents who think it’s the best long-term investment is still below the record high of 34% in 2011. Back then, gold investors sought refuge amid high unemployment, a crippled housing market and volatile stocks, Gallup noted.
Gold prices have been trending upward this spring. Spot gold prices hit an all-time high of above $3,500 per ounce in late April. One year ago, prices were about $2,200 to $2,300 an ounce.
Real estate has also drawn more interest in recent years amid high demand from buyers and accelerating prices. The median sale price for an existing home in the U.S. in March was $403,700, according to Bankrate. That is down from the record high of $426,900 in June.
Why stocks are the better bet
While real estate and gold are two assets that can appreciate in value over time, the stock market will generally grow at a much higher rate, experts say.
The annualized total return of S&P 500 stocks is 10.29% over the 30-year period ending in April, per Morningstar Direct data. Over the same time frame, the annualized total return for real estate is 8.78% and for gold, 7.38%.
McClanahan also points out that unlike gold and real estate, stocks are diversified assets, meaning you’re spreading out your cash versus concentrating it into one investment.
“When you talk about stocks, you’re not talking about one big asset,” she said. “You’re talking about thousands and thousands of companies that do different things.” McClanahan is also a member of the CNBC FA Council.
While the tangibility of gold and real estate may provide a sense of comfort, it also makes them illiquid, or difficult to cash out, McClanahan said.
How to include gold, real estate into your portfolio
If you are among the Americans that want exposure to real estate or gold, there are different ways to do it wisely, experts say.
For real estate, financial advisors say investors might look into real estate investment trusts, also known as REITs, or consider investments that bundle real estate stocks, like exchange-traded funds.
An REIT is a publicly traded company that invests in different types of income-producing residential or commercial real estate, such as apartments or office buildings.
In many cases, you can buy shares of publicly traded REITs like you would a stock, or shares of a REIT mutual fund or exchange-traded fund. REIT investors typically make money through dividend payments.
Real estate mutual funds and exchange-traded funds will typically invest in multiple REITs and in the real estate market broadly. It’s even more diversified than investing in a single REIT.
Either way, you’re exposed to real estate without concentrating into a single property, and it will help diversify your portfolio, McClanahan said.
Similar to gold — instead of stocking up on gold bullions, consider investing in gold through ETFs.
That way you avoid having to deal with finding a place to store or hide physical gold, you wash off the stress of it getting stolen or making sure it’s covered by your home insurance policy, experts say.
“With the ETF, you actually get the value of the return of gold, but you don’t actually own it,” McClanahan said.


 Finance1 week ago
Finance1 week ago
 Finance1 week ago
Finance1 week ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Accounting1 week ago
Accounting1 week ago