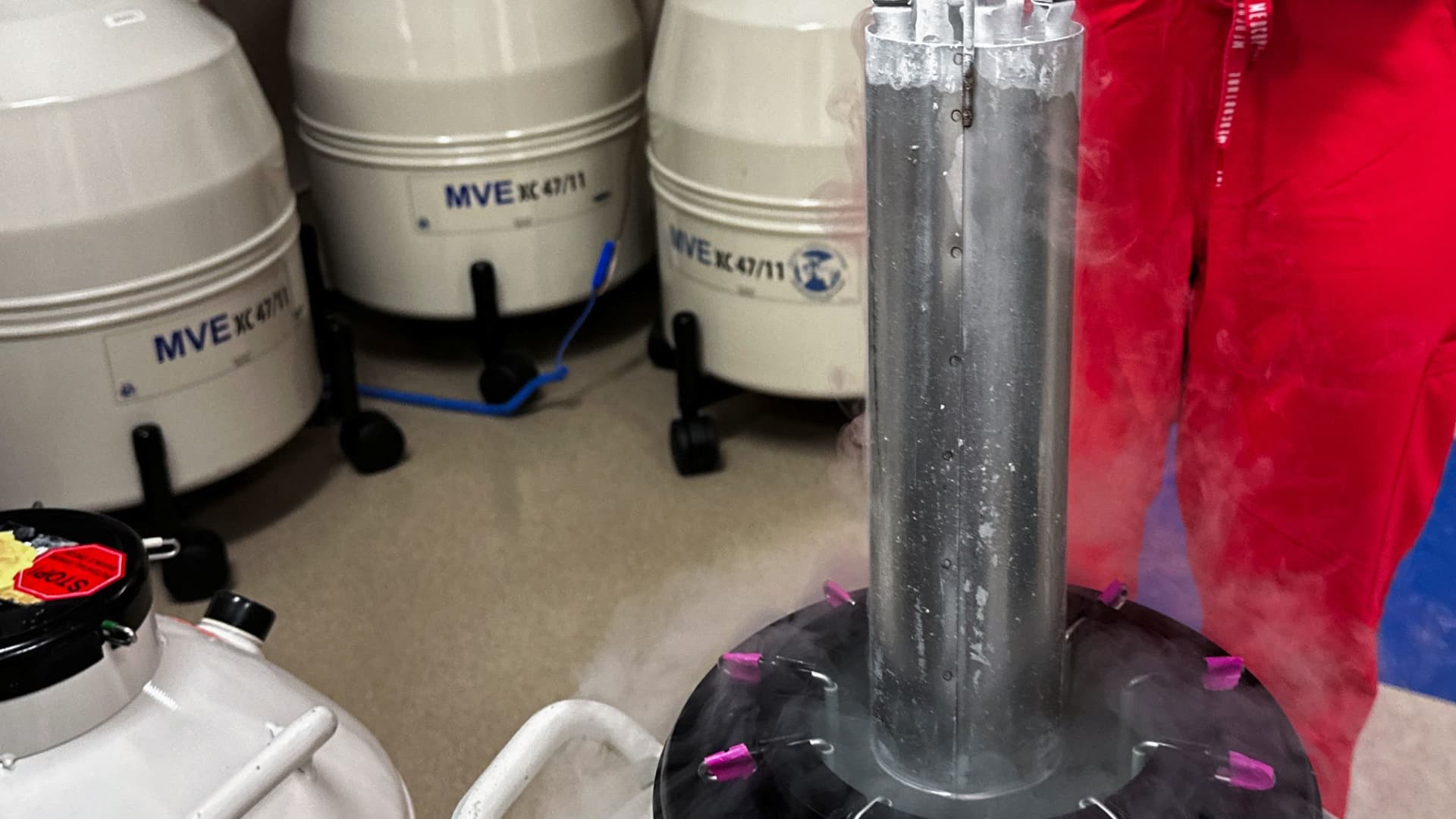
Lynn Curry, nurse practitioner for Huntsville Reproductive Medicine, P.C., lifts frozen embryos out of IVF cryopreservation dewar, in Madison, Alabama, U.S., March 4, 2024.
Roselle Chen | Reuters
As legal battles over reproductive rights increase across the U.S., one area that could be impacted is egg freezing.
In February, the Alabama state Supreme Court ruled that all embryos created through in vitro fertilization are considered children. This ruling could have far-reaching ramifications of civil and criminal liabilities for fertility clinics and their patients. Over 1 million frozen eggs and embryos are stored in the United States alone, according to biotech fertility company TMRW Life Sciences.
Women who choose to undergo reproductive technology procedures such as egg freezing face a long road riddled with obstacles. Here’s a look into the driving forces behind egg freezing and the financial, social and emotional costs that come with it — based on personal experiences from women across the country.
The ‘mating gap’: What’s driving egg freezing
There’s a notion that most women delaying motherhood are doing so to focus on other aspects of their lives, such as their careers. That’s not so much the case anymore, according to Marcia Inhorn, a professor specializing in medical anthropology at Yale University.
“The majority of women who freeze their eggs are doing it because they have not found a partner. I call that the mating gap — the lack of eligible, educated, equal partners,” Inhorn, who last year authored the book “Motherhood on Ice: The Mating Gap and Why Women Freeze Their Eggs,” told CNBC.
This problem stems from the fact that today, women are receiving higher education at greater rates than men. Inhorn noted that women are outperforming men in higher education in 60% of countries, and that in the United States alone there are 27% more women than men in higher education.
“The result is that, for women who are highly educated in America and of reproductive age — between 20 and 39 — there literally are millions too few college-educated men,” Inhorn added.
Another reason women freeze their eggs is the sense of empowerment the procedure brings them. Fundamentally, Inhorn believes that this freedom that egg freezing allows is what ultimately draws increasingly younger women to the procedure.
“It gives you a little reprieve, a little extra time,” she said.
This statement is one that reproductive endocrinologists and fertility specialists Drs. Nicole Noyes and Aimee Eyvazzadeh agree with.
Noyes, who has worked in the fertility industry since 2004 and is based in New York, has seen a noticeable shift in her patients’ ages and attitudes in the last two decades. In the beginning, her patients tended to be older, in their early 40s and viewed egg freezing as a last-ditch procedure as they hedged the end of their reproductive lives. Now, women as young as their late 20s come in to see Noyes.
Eyvazzadeh, who has also worked in the field for 20 years and lives in California, has noticed a trend towards younger patients who are choosing to freeze their eggs while they’re at their most viable.
This is the case for social media influencer Serena Kerrigan, who just recently turned 30. Despite being in a relationship, egg freezing was a procedure she willingly undertook while focusing on growing her business, she told CNBC.
Kerrigan, who has more than 800,000 followers between her Instagram and TikTok and is based in New York, began sharing her egg freezing journey last year. She wanted to remove some of the stigma around egg freezing and give her followers an inside look at the arduous process.
Kerrigan has paid for all her procedures on her own, she told CNBC, and recently partnered with her clinic, Spring Fertility, to donate a round of egg freezing to one of her followers. Eventually, she hopes egg freezing can be less stigmatized.
“There’s a layer of shame or taboo that I actually don’t understand. To me, this is science, and this is incredible, and this is a huge advancement,” she said. “This is a way of putting the power back into women and having control of their lives.”
The benefits are high, but so are the costs
While the benefits of egg freezing are certainly enormous, so too are the associated costs.
The average price for a single egg freezing cycle in the U.S. clocks in at $11,000. Many women need multiple egg freezing cycles, especially as they grow older and egg number and quality begin to deteriorate. That’s not to mention additional charges like hormone medication and yearly storage fees, which could respectively clock in at around $5,000 and $2,000.
Nutrition health coach Jenny Hayes Edwards froze her eggs in 2010 at 34 years old and was one of the first women in the U.S. to undergo the procedure. Despite it still being labeled an “experimental” procedure in the U.S., Hayes Edwards was certain she wanted to try. She wasn’t dating anybody at the time and was “working like crazy” while running her restaurant businesses in Colorado.
But high costs were her number one obstacle. Her restaurants had taken a hit after the 2008 financial collapse, when many consumers began foregoing their expensive ski vacations in Colorado.
Hayes Edwards remembers it being a tough decision to make. But her mother eventually helped sway her in favor of the procedure.
“It’s just money, and the opportunity that you might be missing is so much bigger,” Hayes Edwards recalled her mother saying. “I was so grateful that she pushed me over the edge.”
She was able to scrape together the $15,000 needed through maxing out a credit card, selling some jewelry and liquidating a bond in her inheritance.
Hayes Edwards now has a healthy three-year-old daughter, conceived nearly a decade after she froze her eggs, and is still appreciative for the extra time egg freezing bought her to meet her now-husband.
Employer benefits
In recent years, egg freezing, fertility and family planning services have increasingly popped up as employer benefits, especially among technology companies. A 2021 study from Mercer showed 42% of large companies — those with at least 20,000 employees — covered in vitro fertilization services in 2020, up from 36% in 2015. Nineteen-percent of these companies had egg freezing benefits, more than triple the 6% offering these benefits in 2015.
Michelle Parsons decided to freeze her eggs since the procedure was offered through her job. The various tech companies Parsons has worked for have offered anywhere between $10,000 to $75,000 in fertility benefits.
Parsons, who is a lesbian, had always known that she wanted to freeze her eggs — and undertook the procedure while working at Match Group as chief product officer of dating app Hinge. At the time, neither she nor her ex-partner were ready to have children, but it was one financial incentive Parsons didn’t want to miss out on.
Besides eggs, Parsons also chose to freeze her successfully fertilized embryos as another backup. Frozen embryos have a much higher likelihood of viable thawing. In fact, Parsons’ search for a sperm donor sparked one of the most-used features on the Hinge app — voice prompts.
“When we started to listen to all of these voice recordings of potential sperm donors, the lightbulb went off in my head and I was like, wow, this is what’s missing from dating right now,” Parsons told CNBC. “Because voice gives you so much nuance into personality, humor, vibe … we ended up building that feature called voice prompts on Hinge and it was a huge, wild success that led to rapid growth for Hinge and it became viral on TikTok.”
Still, Parsons noticed egg freezing taking a toll on her professional and personal life in other ways.
“You have to inject yourself with hormones for two weeks. You have to eat differently. You don’t really want to be in social settings. You can’t drink. There are all these other ramifications around just going through that process, even though we know it’ll be for this one month and then it’ll be over,” she said.
The process also doesn’t guarantee success.
Evelyn Gosnell underwent her first egg retrieval when she was 32, following by two additional cycles at 36 and 38 years old. By the time she was ready to have children with her now-partner, the New York-based behavioral scientist had many frozen eggs ready. But, she received no viable and normal embryos after her eggs had been thawed and fertilized.

 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Blog Post1 week ago
Blog Post1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics7 days ago
Economics7 days ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago