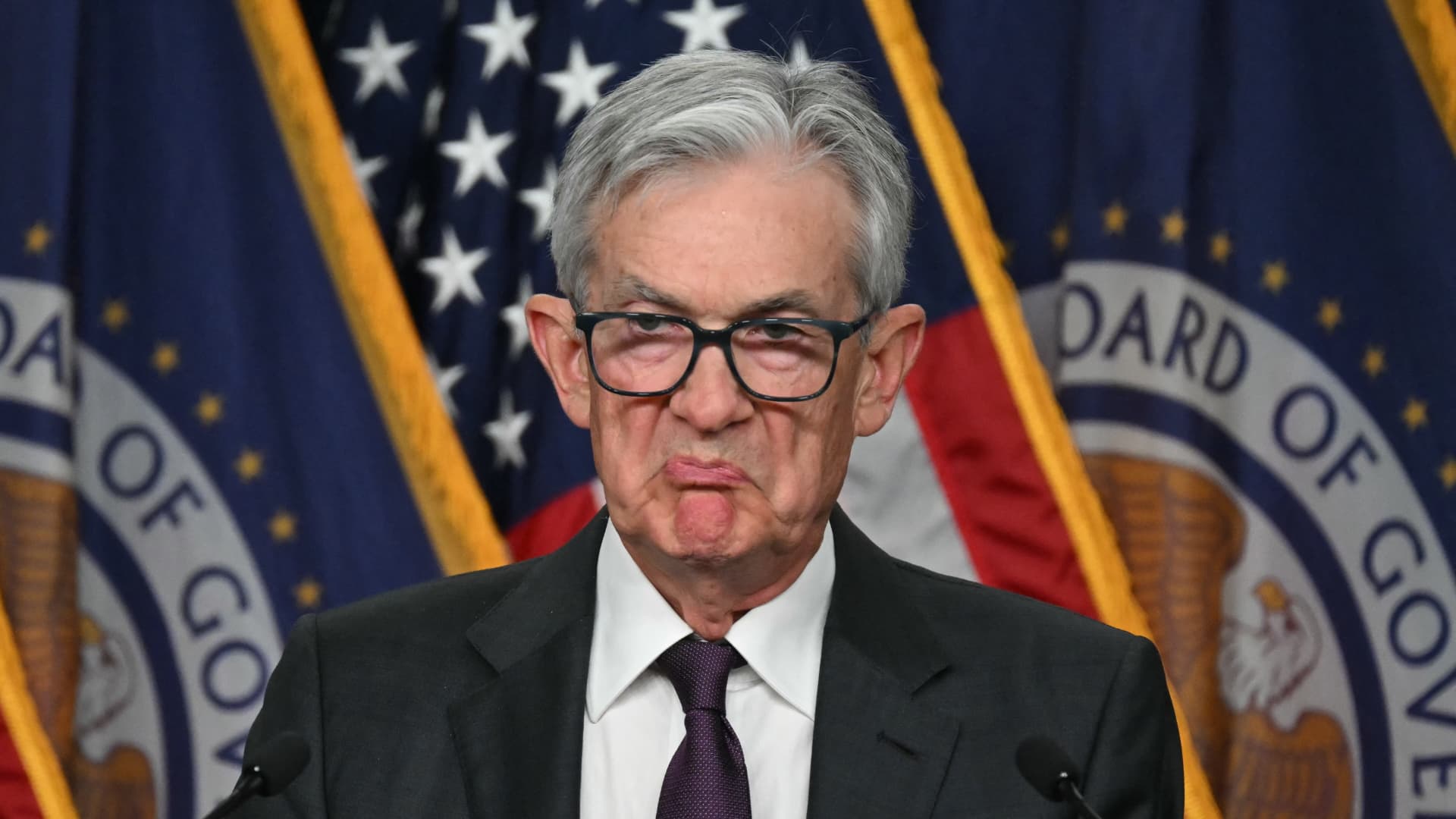
US Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell reacts as he speaks during a news conference at the end of the two-day Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meeting at the Federal Reserve in Washington, DC, on Jan. 29, 2025.
Andrew Caballero-Reynolds | AFP | Getty Images
Federal Reserve officials at this week’s meeting are expected to hold interest rates steady but adjust their views on the economy and possibly the future path for interest rates.
If market pricing is correct, there’s virtually no chance central bank policymakers budge from the current level of their key interest rate, targeted in a range between 4.25%-4.5%. Chair Jerome Powell and his colleagues in recent weeks have advocated a patient approach in which they don’t need to be in a hurry to do anything.
However, they are also expected to drop clues about where things go from here against the uncertain backdrop of President Donald Trump‘s trade and fiscal policies. That could include anything from tweaks in projections for inflation and economic growth to how often, if at all, they expect to lower interest rates further.
“There’s no chance of a cut Wednesday, so all the other stuff becomes more important,” said Dan North, senior economist at Allianz Trade North America. “They’re basically going to say, ‘You know what, we are in no hurry at all now.'”
Indeed, that has been the prevailing message from Powell and his Federal Open Market Committee colleagues. In a speech earlier this month to economists in New York, Powell insisted “there is no need to be in a hurry” as central bankers seek “greater clarity” on where the Trump administration is headed.
New outlook for GDP, inflation, unemployment
The public, then, will be left to pore through updates the Fed makes to its quarterly projections on interest rates, gross domestic product, unemployment and inflation. Based on recent data, the Fed could raise its 2025 outlook for inflation (in December, the outlook was for 2.5% in both core and headline) while lowering its GDP projection (from 2.1%). Powell will host his usual post-meeting news conference.
On the rate question, the Federal Open Market Committee will use its “dot plot” grid of individual members’ intentions.
There’s significant disagreement on what could happen there. The committee could maintain its December outlook for two cuts, remove one or both, or, improbably, add another as a statement of concern over a potential slowdown. Everything seems to be on the table.
“I think it may be one or zero cuts this year, particularly if the tariffs stick,” North said. “I don’t think they’re going to try and bail out the economy by cutting rates, because they know that if they stoke inflation, they’re going to have to go back and start all over again.”
Economists worry the Trump tariffs could reignite inflation, particularly if the president gets more aggressive after the White House releases a global review of the tariff situation on April 2. If the Fed grows more concerned about tariff-fueled inflation, it could turn even more reluctant to cut.
Investors are right to be concerned about the direction the FOMC indicates, said Thierry Wizman, global FX and rates strategist at Macquarie.
“That worry is borne by the suspicion the Fed is not ‘in charge’ anymore, having relinquished control of macroeconomic policy to the Trump administration,” Wizman wrote. “Given the current uncertainty, and the recent increase in inflation expectations, the Fed may find it difficult to signal three more rate cuts, or even two more. It could push one rate cut into 2026, leaving only one cut in the median ‘dot’ for 2025.”
Markets still see two or three cuts
Should the Fed decide to stick with two cuts, it likely will be only “to avoid adding to recent market turbulence,” Goldman Sachs economist David Mericle said in a note.
Major stock market averages are hovering around correction territory, or 10% declines from highs.
In the past, under the idea of a “Fed put,” markets have come to expect the central bank to ease policy in response to market unrest. Traders don’t expect an initial rate reduction to happen until at least June, and are pricing in one additional quarter percentage point easing and about a 50-50 chance of a third move by the end of the year, according to the CME Group’s FedWatch measure of fed funds futures pricing.
But that might even be too ambitious, Wizman said.
“In effect, markets appear to have gotten too dovish on the Fed, and instead of signaling its own confidence in its outlook, the Fed may issue signals of no-confidence, instead. In other words, the FOMC meeting may leave many questions unanswered, as will the press conference by Jay Powell,” he said, using Powell’s nickname.
The committee also could address its “quantitative tightening” program where it is allowing a set level of proceeds from maturing bonds to roll off the balance sheet each month. Markets widely expect the Fed to end the program later this year, and recent meetings have featured discussion about how best to handle the central bank’s $6.4 trillion portfolio of Treasurys and mortgage-backed securities.

 Accounting6 days ago
Accounting6 days ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Personal Finance6 days ago
Personal Finance6 days ago
 Accounting6 days ago
Accounting6 days ago
 Finance5 days ago
Finance5 days ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics6 days ago
Economics6 days ago
 Economics6 days ago
Economics6 days ago