U.S. economic growth was much weaker than expected to start the year, and prices rose at a faster pace, the Commerce Department reported Thursday.
Gross domestic product, a broad measure of goods and services produced in the January-through-March period, increased at a 1.6% annualized pace when adjusted for seasonality and inflation, according to the department’s Bureau of Economic Analysis.
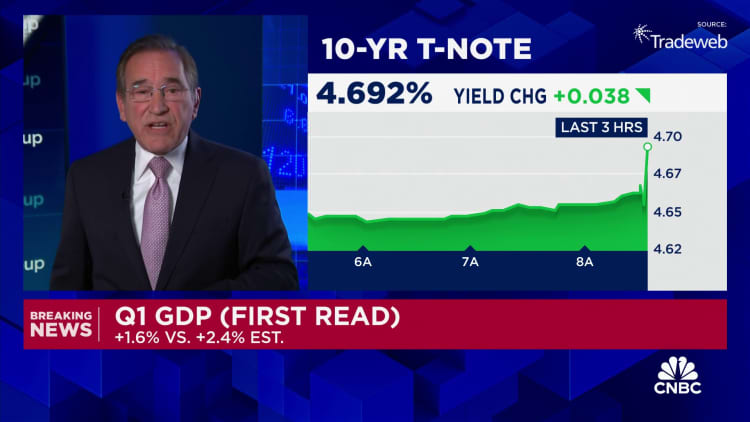
Economists surveyed by Dow Jones had been looking for an increase of 2.4% following a 3.4% gain in the fourth quarter of 2023 and 4.9% in the previous period.
Consumer spending increased 2.5% in the period, down from a 3.3% gain in the fourth quarter and below the 3% Wall Street estimate. Fixed investment and government spending at the state and local level helped keep GDP positive on the quarter, while a decline in private inventory investment and an increase in imports subtracted. Net exports subtracted 0.86 percentage points from the growth rate while consumer spending contributed 1.68 percentage points.
There was some bad news on the inflation front as well.
The personal consumption expenditures price index, a key inflation variable for the Federal Reserve, rose at a 3.4% annualized pace for the quarter, its biggest gain in a year and up from 1.8% in the fourth quarter. Excluding food and energy, core PCE prices rose at a 3.7% rate, both well above the Fed’s 2% target. Central bank officials tend to focus on core inflation as a stronger indicator of long-term trends.
The price index for GDP, sometimes called the “chain-weighted” level, increased at a 3.1% rate, compared to the Dow Jones estimate for a 3% increase.
Markets slumped following the news, with futures tied to the Dow Jones Industrial Average off more than 400 points. Treasury yields moved higher, with the benchmark 10-year note most recently at 4.69%.
“This was a worst of both worlds report – slower than expected growth, higher than expected inflation,” said David Donabedian, chief investment officer of CIBC Private Wealth US. “We are not far from all rate cuts being backed out of investor expectations. It forces [Fed Chair Jerome] Powell into a hawkish tone for next week’s [Federal Open Market Committee] meeting.”
The report comes with markets on edge about the state of monetary policy and when the Federal Reserve will start cutting its benchmark interest rate. The federal funds rate, which sets what banks charge each other for overnight lending, is in a targeted range between 5.25%-5.5%, the highest in some 23 years though the central bank has not hiked since July 2023.
Investors have had to adjust their view of when the Fed will start easing as inflation has remained elevated. The view as expressed through futures trading is that rate reductions will begin in September, with the Fed likely to cut just one or two times this year. Futures pricing also shifted after the GDP release, with traders now pointing to just one cut in 2024, according to CME Group calculations.
“The economy will likely decelerate further in the following quarters as consumers are likely near the end of their spending splurge,” said Jeffrey Roach, chief economist at LPL Financial. “Savings rates are falling as sticky inflation puts greater pressure on the consumer. We should expect inflation will ease throughout this year as aggregate demand slows, although the path to the Fed’s 2% target still looks a long ways off.”
Consumers generally have kept up with inflation since it began spiking, though rising inflation has eaten into pay increases. The personal savings rate decelerated in the first quarter to 3.6% from 4% in Q4. Income adjusted for taxes and inflation rose 1.1% for the period, down from 2%.
Spending patterns also shifted in the quarter. Spending on goods declined 0.4%, in large part to a 1.2% slide in bigger-ticket purchases for long-lasting items classified as durable goods. Services spending increased 4%, its highest quarterly level since Q3 of 2021.
A buoyant labor market has helped underpin the economy. The Labor Department reported Thursday that initial jobless claims totaled 207,000 for the week of April 20, down 5,000 and below the 215,000 estimate.
In a possible positive sign for the housing market, residential investment surged 13.9%, its largest increase since the fourth quarter of 2020.
Thursday’s release was the first of three tabulations the BEA does for GDP. First-quarter readings can be subject to substantial revisions — in 2023, the initial Q1 reading was an increase of just 1.1% that ultimately was taken up to 2.2%.

 Accounting1 week ago
Accounting1 week ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Accounting1 week ago
Accounting1 week ago
 Finance1 week ago
Finance1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago