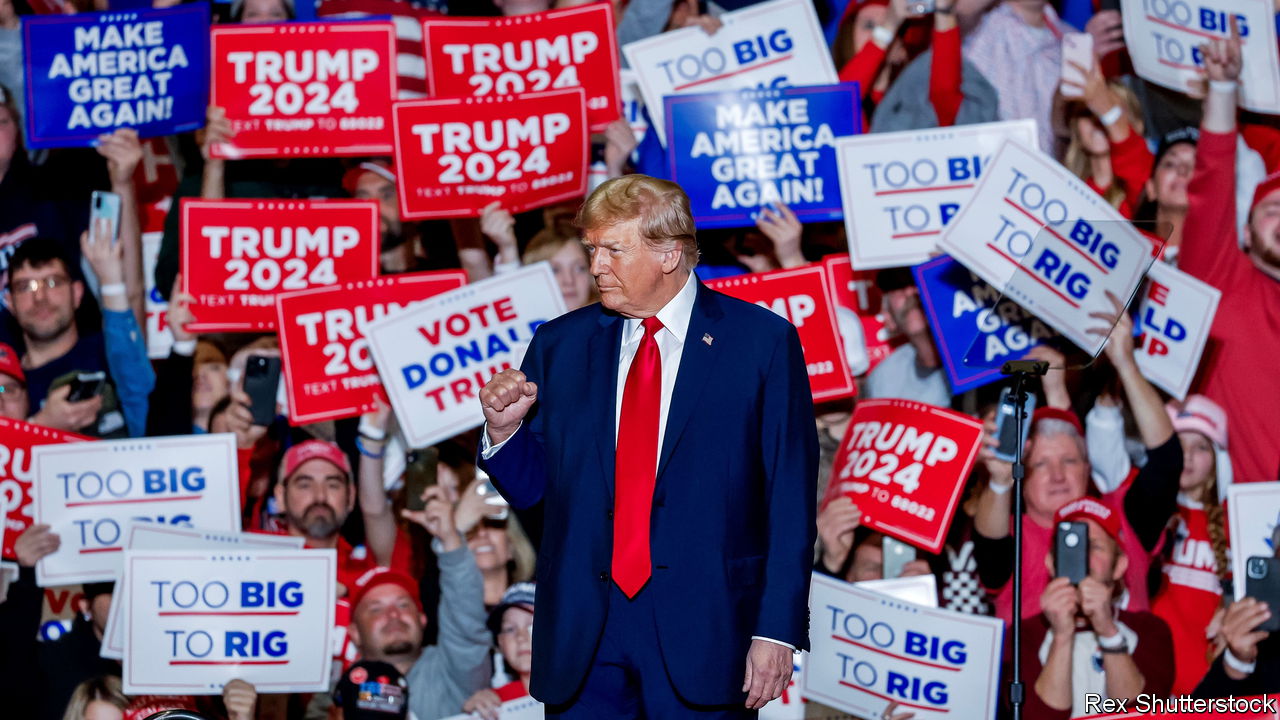
AN OBSCURE patch of the constitution from 1868 never looked likely to keep Donald Trump off the presidential ballot in 2024. It was not clear that the idea of turning to Section 3 of the 14th Amendment—which bars officials who engage in “insurrection or rebellion” from holding future office—would gain traction in any of the 35 states where lawsuits emerged. But litigants had a viable claim: after taking an oath to protect the constitution, the 45th president had arguably thwarted the peaceful transfer of power on January 6th 2021 and was therefore (according to Section 3) barred from recapturing the presidency. Judges and officials in Colorado, Maine and—just last week—Illinois found this reasoning persuasive.
On March 4th, a day before Colorado and 15 other states are set to vote in primaries on Super Tuesday, the Supreme Court punctured any remaining hopes that the post-civil-war provision (originally designed to keep former Confederates at bay) would stop Mr Trump’s third run for the White House.
The justices voted unanimously to reverse the Colorado Supreme Court’s ruling that disqualified Mr Trump from the state’s primary ballot. They had given strong hints in the hearing on February 8th. Justices from right to left said that states may not unilaterally erase presidential candidates from the ballot because they are purported insurrectionists.
The decision is “per-curiam” (“by the court”) with no noted author. It proceeds on the premise that the 14th Amendment was intended primarily to restrict state autonomy—an emphasis that militates against giving states latitude to remove candidates themselves. The opinion also leans heavily on Section 5 of the amendment, which assigns to Congress the “power to enforce” the amendment’s many guarantees (from the “equal protection of the laws” to the bar on unduly depriving people of “life, liberty or property”). It is fine, the court notes, for states to disqualify candidates for state office. But “with respect to federal offices, especially the presidency”, the constitution “does not affirmatively delegate such a power to the states”.
The court writes that “state-by-state resolution” of the disqualification question “would be quite unlikely to yield a uniform answer” across the country. The “patchwork” that would result “could dramatically change the behaviour of voters, parties, and states across the country”, potentially “nullify[ing] the votes of millions and chang[ing] the election result”. The constitution cannot be read to impose such “chaos” on the country.
Although the decision was unanimous, the four female justices criticised their five male colleagues for deciding more than they needed to—and foreclosing other methods of enforcing Section 3. Justice Amy Coney Barrett wrote that the case “does not require us to address the complicated question whether federal legislation is the exclusive vehicle through which Section 3 can be enforced”. For Justices Ketanji Brown Jackson, Elena Kagan and Sonia Sotomayor, the opinion could have started and ended with the proposition that empowering Colorado to remove Mr Trump from the ballot risked “a chaotic state-by-state patchwork, at odds with our nation’s federalism principles”. In their view, the five men were excessively bold, deciding “novel constitutional questions” that rope off future challenges under Section 3.
The majority went further than necessary, the court’s three liberal justices charged, “creat[ing] a special rule for the insurrection disability in Section 3” that does not apply to any other provision of the 14th Amendment. There is “next to no support” for the proposition that Congress must pass a statute to enforce Section 3, the opinion continues. By overreaching, the court in effect “insulate[s] all alleged insurrectionists from future challenges to their holding federal office” and “shuts the door on other potential means of federal enforcement”—in a federal court, say, or via an act of Congress that is, in the eyes of a future Supreme Court majority, disproportionate or incongruent.
These disagreements mean that Trump v Anderson goes down as both a unanimous decision barring Colorado from removing Mr Trump and a 5-4 ruling giving the Supreme Court final say on congressional action disqualifying any oath-breaking insurrectionist from pursuing public office. But for the leading Republican candidate for president, the message is clear: full steam ahead. ■

 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Blog Post1 week ago
Blog Post1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics6 days ago
Economics6 days ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago