Eric Thayer/Bloomberg via Getty Images
Inflation jumped in March as prices for consumer staples like gasoline edged higher and those for housing remain stubbornly high, suggesting inflation may be a bit stickier than seemed just a few months ago, economists said.
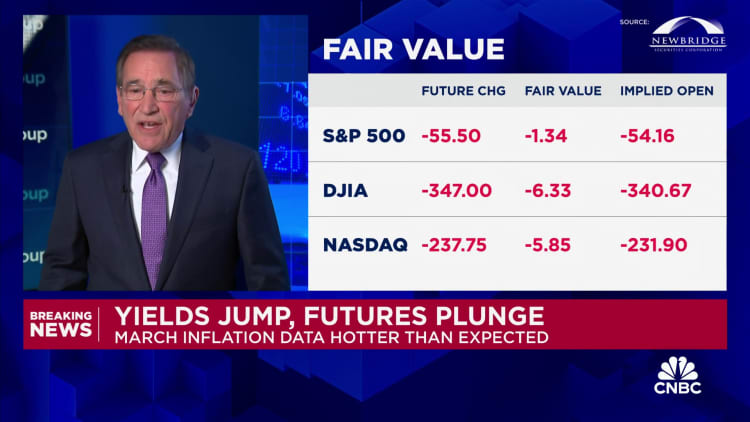
The consumer price index, a key inflation gauge, rose 3.5% in March from a year ago, the U.S. Labor Department reported Wednesday. That’s up from 3.2% in February.
CPI measures how fast prices are changing across the U.S. economy. It measures everything from fruits and vegetables to haircuts, concert tickets and household appliances.
The March inflation reading is down significantly from its 9.1% pandemic-era peak in 2022, which was the highest level since 1981. However, it remains above policymakers’ long-term target around 2%.
Progress in the inflation fight has somewhat flatlined in recent months.
“The disinflation has stalled out,” said Mark Zandi, chief economist at Moody’s Analytics.
“The big rock in the way here is the cost of shelter,” Zandi said.
While housing costs have moderated, they account for the largest share of the CPI inflation index and “are still growing strongly,” he added.
Despite progress having stalled, broader evidence doesn’t suggest a renewed surge in inflation — though it may take longer than expected to bring the rate back to target, economists said. In fact, underlying inflation after stripping out shelter costs is already back to target, Zandi said.
“I still hold to the view that inflation is moderating,” Zandi said. “It’s just taking frustratingly long to get there.”
Household paychecks can buy more stuff, though
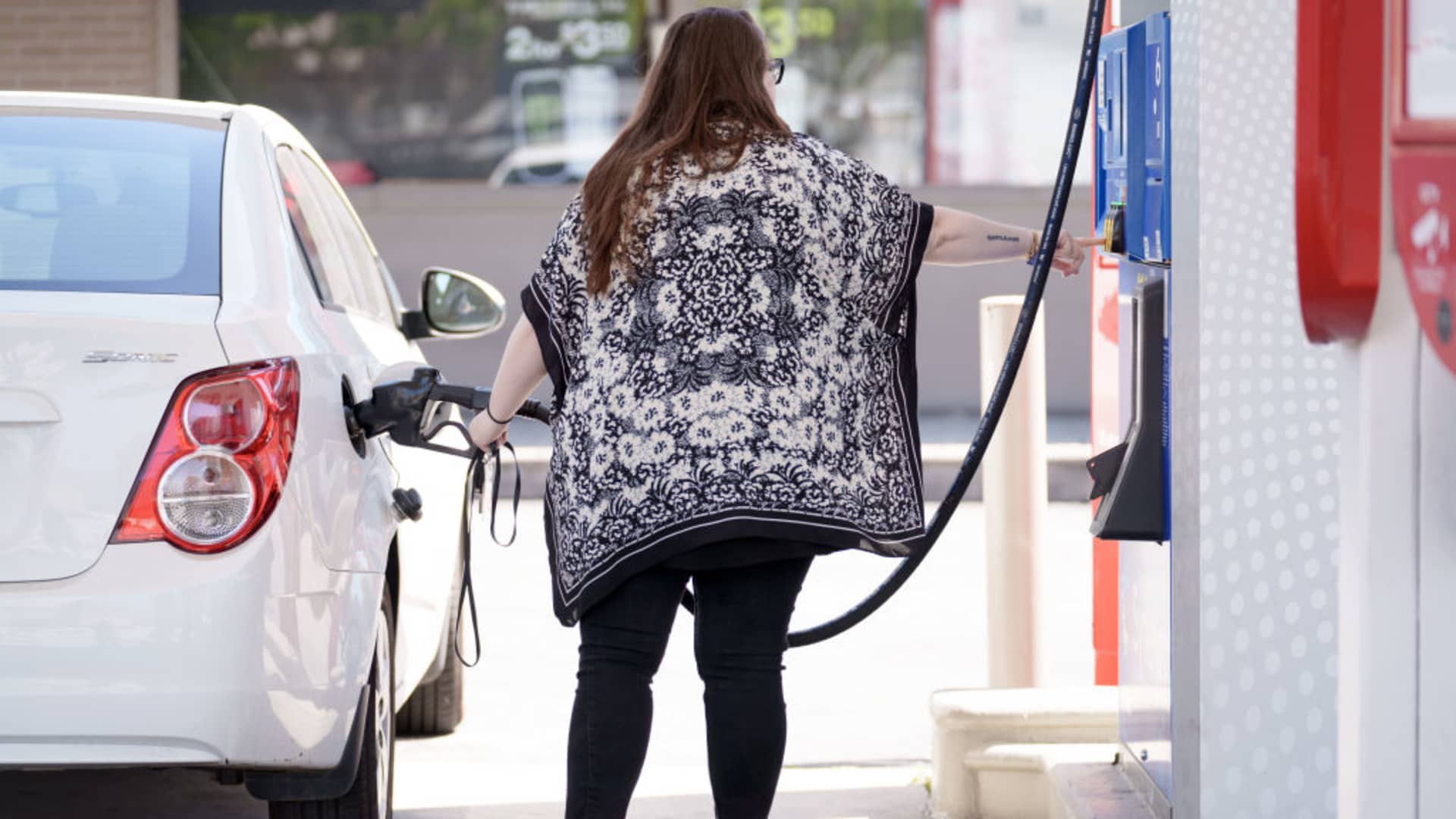
Higher oil and gas prices take a toll
Gasoline prices increased 1.7% from February to March, the Bureau of Labor Statistics said. (This figure is adjusted to account for seasonal buying patterns.)
Average U.S. pump prices were $3.52 a gallon on April 1, up from $3.35 on March 4, according weekly data published by the Energy Information Administration.
The increase is largely attributable to higher oil prices. They’ve firmed amid a generally positive outlook for the global economy (meaning greater global oil demand) and controlled output among major oil-producing nations (meaning there hasn’t been a glut of oil), economists said.
Tensions in the Middle East may also be playing a role, Hamrick said.
Higher gas prices may filter through to higher prices elsewhere, since they factor into transportation and distribution costs for goods and even services like food delivery, he said.
Higher energy prices are what worries Zandi most relative to inflation readings. It’s likely the upward trend will continue in coming months, and the dynamic negatively impacts consumer buying power and sentiment, he said.
“Nothing does more damage to the economy more quickly than rising oil and gasoline prices,” he said.
Other ‘notable’ areas of inflation
In addition to shelter, motor vehicle insurance, medical care, recreation and personal care were “notable” contributors to “core” inflation (a reading that strips out volatile energy and food prices), the BLS said.
Shelter, motor vehicle insurance, medical care, apparel and personal care were notable contributors to monthly inflation from February to March, the agency said.
The overall monthly CPI reading, 0.4%, was much higher than the roughly 0.2% that would be expected on a consistently basis to bring inflation back to normal, economists said.
“There is no improvement here; we’re moving in the wrong direction,” Hamrick said.
“The usual trouble spots persist,” said Hamrick, who additionally called out costs for electricity and car maintenance and repairs.
Prices have fallen in some categories
Meanwhile, some consumer categories have seen improvement.
Prices fell for used cars and trucks, new vehicles and airline tickets between February and March, for example. They’re also down over the past year, by 2.2%, 0.1% and 7.1%, respectively, according to CPI data.
Lower prices for new and used cars should lead auto insurance and repair costs to fall as well, economists said.
Grocery prices are another bright spot, they said.
While some categories like eggs and pork chops have seen recent upward movement, the overall “food at home” index stood at 0% on a monthly basis in both February and March.
“Food prices have come to a standstill,” Zandi said. “For most Americans, the thing that bothers them the most about inflation is high food prices.”
Out-of-whack supply and demand
At a high level, supply-and-demand imbalances are what trigger out-of-whack inflation.
For example, the Covid-19 pandemic disrupted supply chains for goods. Americans’ buying patterns also simultaneously shifted away from services — like entertainment and travel — toward physical goods since they stayed at home more, driving up demand and fueling decades-high goods inflation.
Additionally, supply-and-demand dynamics in the labor market pushed wage growth to the highest level in decades, putting upward pressure on prices for services, which are more wage-sensitive.
Now that supply-chain issues are “pretty close to fixed,” there’s “little scope” for goods to contribute to disinflation moving forward, said Sarah House, senior economist at Wells Fargo Economics.
“You need services to take the mantle of disinflation,” because goods have “petered out,” she added.
Housing falls in the services category. It accounts for the largest share of the consumer price index, so disinflation in this category would likely have a large impact on inflation readings.
So far, housing inflation has remained stubbornly high — even as economists have predicted it would start moderating any day given broadly positive trends in prices for new tenant rental leases, for example.
“It seems to be taking a bit longer than people thought,” said Andrew Hunter, deputy chief U.S. economist at Capital Economics.
“It’s coming,” he said. “It’s just a matter of when.”


 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Blog Post1 week ago
Blog Post1 week ago
 Accounting1 week ago
Accounting1 week ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Personal Finance6 days ago
Personal Finance6 days ago
 Economics6 days ago
Economics6 days ago
 Personal Finance6 days ago
Personal Finance6 days ago
 Finance6 days ago
Finance6 days ago