The U.S. economy added fewer jobs than expected in April while the unemployment rate rose, lifting hopes that the Federal Reserve will be able to cut interest rates in the coming months.
Nonfarm payrolls increased by 175,000 on the month, below the 240,000 estimate from the Dow Jones consensus, the Labor Department’s Bureau of Labor Statistics reported Friday. The unemployment rate ticked higher to 3.9% against expectations it would hold steady at 3.8%.
Average hourly earnings rose 0.2% from the previous month and 3.9% from a year ago, both below consensus estimates and an encouraging sign for inflation.
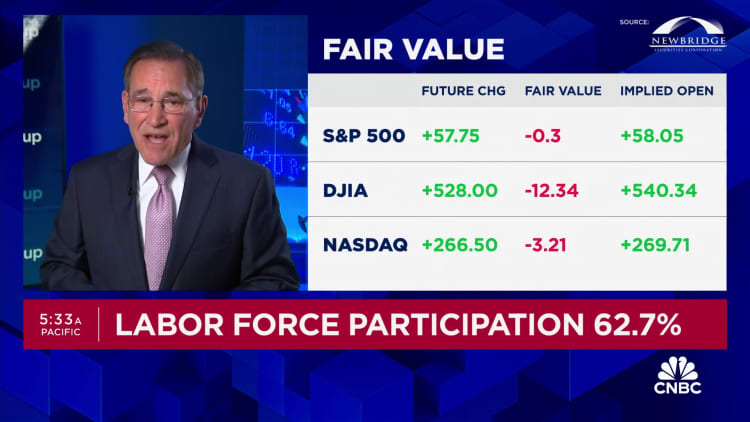
The jobless rate tied for the highest level since January 2022. A more encompassing rate that includes discouraged workers and those holding part-time jobs for economic reasons also edged up, to 7.4%, its highest level since November 2021. The labor force participation rate, or those actively looking for work, was unchanged at 62.7%.
Wall Street already had been poised for a higher open, and futures tied to major stock market averages added to gains following the report. Treasury yields tumbled after being little changed before the release. The report raised the prospect of a “Goldilocks” climate where growth continues but not at such a rapid pace to force the Fed to tighten policy further.
“With this report, the porridge was just about right,” said Dan North, senior economist at Allianz Trade. “What would you like at this point the cycle? We’ve had interest rates jacked up pretty high, so you would expect to see the labor market slow down a little. But we’re still at pretty high levels.”
Consistent with recent trends, health care led job creation, with a 56,000 increase.
Other sectors showing significant rises included social assistance (31,000), transportation and warehousing (22,000), and retail (20,000). Construction added 9,000 positions while government, which had shown solid gains in recent months, was up just 8,000 after averaging 55,000 over the previous 12 months.
Revisions to previous months took the March gain to 315,000, or 12,000 from the initial estimate, and February to 236,000, a decline of 34,000.
Household employment, which is used to calculate the unemployment rate, increased by just 25,000 on the month. Workers holding full-time jobs soared by 949,000 on the month, while those hold part-time jobs slumped by 914,000.
The report comes two days after the Fed again voted to hold borrowing costs steady, keeping its benchmark overnight borrowing rate in a targeted range between 5.25%-5.5%, the highest in more than 20 years.
Following the decision, Chair Jerome Powell characterized the jobs market as “strong” but noted that inflation is “too high” and this year’s economic data has indicated “a lack of further progress” in getting inflation back to the Fed’s 2% target.
But market action shifted after the jobs report indicated an easing labor market and softer wage increases. Traders priced in a strong chance of two interest rate cuts by the end of 2024, with the first reduction expected to come in September, according to CME Group data.
“This is the jobs report the Fed would have scripted,” said Seema Shah, chief global strategist at Principal Asset Management. “The first downside payrolls surprise in several months, as well as the dip in average hourly earnings growth, will bring the rate cutting dialogue back into the market and perhaps explains why Powell was able to be dovish on Wednesday.”
Though inflation has come well off its highs in mid-2022, it is still considerably above the central bank’s comfort zone. Most reports this year have shown inflation around 3% annually; the Fed’s own preferred measure, the core personal consumption expenditures price index, most recently was at 2.8%.
Higher prices have been putting upward pressure on wages, part of an inflation picture that has kept the Fed on the sidelines despite widespread market expectations that the central bank would be cutting interest rates aggressively this year.
Most Fed officials in fact had been mentioning the likelihood of reductions in their public comments. However, Powell at his post-meeting news conference Wednesday made no mention of the likelihood that rates would be lowered at some point this year, as he had in the past.

 Accounting1 week ago
Accounting1 week ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Accounting1 week ago
Accounting1 week ago
 Finance1 week ago
Finance1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago