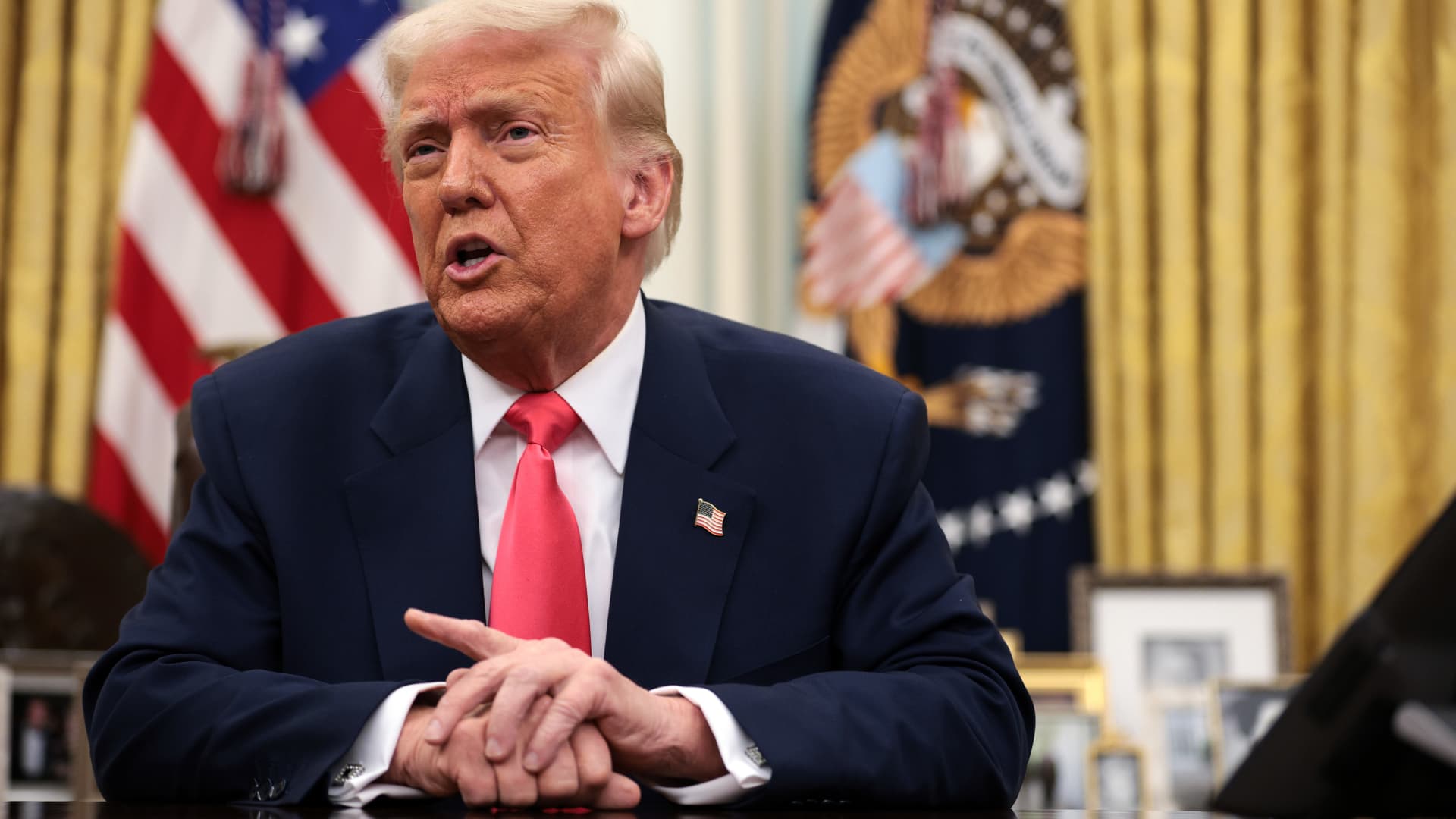
President Donald Trump speaks before signing executive orders in the Oval Office on March 6, 2025.
Alex Wong | Getty Images
President Donald Trump says that tariffs will make the U.S. “rich.” But those riches will likely be far less than the White House expects, economists said.
The ultimate sum could have big ramifications for the U.S. economy, the nation’s debt and legislative negotiations over a tax-cut package, economists said.
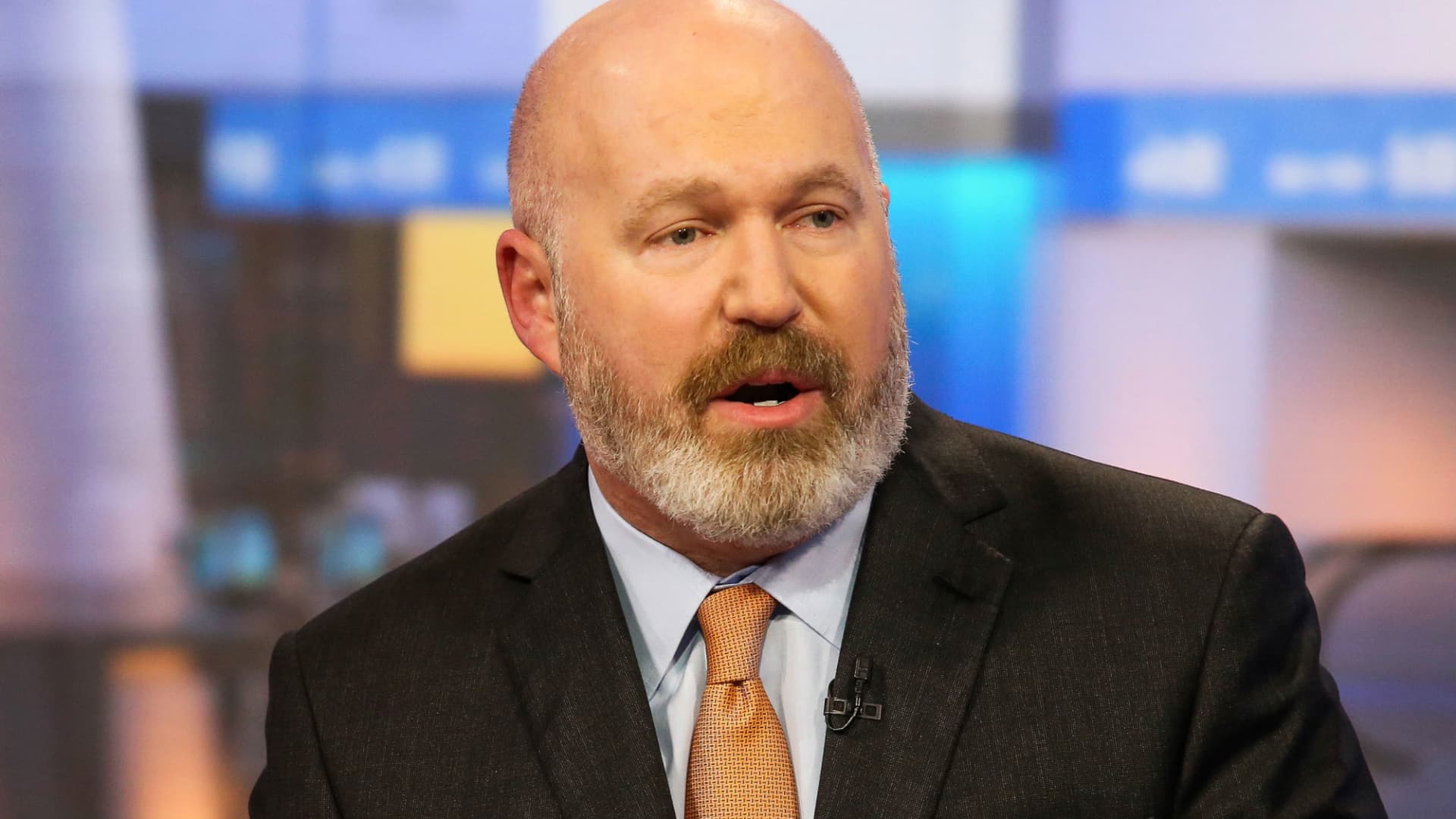
White House trade adviser Peter Navarro on Sunday estimated tariffs would raise about $600 billion a year and $6 trillion over a decade. Auto tariffs would add another $100 billion a year, he said on “Fox News Sunday.”
Navarro made the projection as the U.S. plans to announce more tariffs against U.S. trading partners on Wednesday.
Economists expect the Trump administration’s tariff policy would generate a much lower amount of revenue than Navarro claims. Some project the total revenue would be less than half.
Roughly $600 billion to $700 billion a year “is not even in the realm of possibility,” said Mark Zandi, chief economist at Moody’s. “If you get to $100 billion to $200 billion, you’ll be pretty lucky.”
The White House declined to respond to a request for comment from CNBC about tariff revenue.
The ‘mental math’ behind tariff revenue
There are big question marks over the scope of the tariffs, including details like amount, duration, and products and countries affected — all of which have a significant bearing on the revenue total.
The White House is considering a 20% tariff on most imports, The Washington Post reported on Tuesday. President Trump floated this idea on the campaign trail. The Trump administration may ultimately opt for a different policy, like country-by-country tariffs based on each nation’s respective trade and non-trade barriers.
But a 20% tariff rate seems to align with Navarro’s revenue projections, economists said.
The U.S. imported about $3.3 trillion of goods in 2024. Applying a 20% tariff rate to all these imports would yield about $660 billion of annual revenue.
“That is almost certainly the mental math Peter Navarro is doing — and that mental math skips some crucial steps,” said Ernie Tedeschi, director of economics at the Yale Budget Lab and former chief economist at the White House Council of Economic Advisers during the Biden administration.
Trade advisor to U.S. President Donald Trump Peter Navarro speaks to press outside of the White House on March 12, 2025 in Washington, DC.
Kayla Bartkowski | Getty Images
That’s because an accurate revenue estimate must account for the many economic impacts of tariffs in the U.S. and around the world, economists said. Those effects combine to reduce revenue, they said.
A 20% broad tariff would raise about $250 billion a year (or $2.5 trillion over a decade) when taking those effects into account, according to Tedeschi, citing a Yale Budget Lab analysis published Monday.
There are ways to raise larger sums — but they would involve higher tariff rates, economists said. For example, a 50% across-the-board tariff would raise about $780 billion per year, according to economists at the Peterson Institute for International Economics.
Even that is an optimistic assessment: It doesn’t account for lower U.S. economic growth due to retaliation or the negative growth effects from the tariffs themselves, they wrote.
Why revenue would be lower than expected
Tariffs generally raise prices for consumers. A 20% broad tariff would cost the average consumer $3,400 to $4,200 a year, according to the Yale Budget Lab.
Consumers would naturally buy fewer imported goods if they cost more, economists said. Lower demand means fewer imports and less tariff revenue from those imports, they said.
Tariffs are also expected to trigger “reduced economic activity,” said Robert McClelland, senior fellow at the Urban-Brookings Tax Policy Center.
More from Personal Finance:
Economists say ‘value-added taxes’ aren’t a trade barrier
Tariffs are ‘lose-lose’ for U.S. jobs and industry
Why uncertainty makes the stock market go haywire
For example, U.S. companies that don’t pass tariff costs on to consumers via higher prices would likely see profits suffer (and their income taxes fall), economists said. Consumers might pull back on spending, further denting company profits and tax revenues, economists said. Companies that take a financial hit might lay off workers, they said.
Foreign nations are also expected to retaliate with their own tariffs on U.S. products, which would hurt companies that export products abroad. Other nations may experience an economic downturn, further reducing demand for U.S. products.
“If you get a 20% tariff rate, you’re going to get a rip-roaring recession, and that will undermine your fiscal situation,” Zandi said.
There’s also likely to be a certain level of non-compliance with tariff policy, and carve-outs for certain countries, industries or products, economists said. For instance, when the White House levied tariffs on China in February, it indefinitely exempted “de minimis” imports valued at $800 or less.
The Trump administration might also funnel some tariff revenue to paying certain parties aggrieved by a trade war, economists said.
President Trump did that in his first term: The government sent $61 billion in “relief” payments to American farmers who faced retaliatory tariffs, which was nearly all (92%) of the tariff revenue on Chinese goods from 2018 to 2020, according to the Council on Foreign Relations.
The tariffs will also likely have a short life span, diluting their potential revenue impact, economists said. They’re being issued by executive order and could be undone easily, whether by President Trump or a future president, they said.
“There’s zero probability these tariffs will last for 10 years,” Zandi said. “If they last until next year I’d be very surprised.”
Why this matters
The Trump administration has signaled that tariffs “will be one of the top-tier ways they’ll try to offset the cost” of passing a package of tax cuts, Tedeschi said.
Extending a 2017 tax cut law signed by President Trump would cost $4.5 trillion over a decade, according to the Tax Foundation. Trump has also called for other tax breaks like no taxes on tips, overtime pay or Social Security benefits, and a tax deduction for auto loan interest for American made cars.
If tariffs don’t cover the full cost of such a package, then Republican lawmakers would have to find cuts elsewhere or increase the nation’s debt, economists said.

 Economics5 days ago
Economics5 days ago
 Personal Finance7 days ago
Personal Finance7 days ago
 Economics6 days ago
Economics6 days ago
 Economics5 days ago
Economics5 days ago
 Accounting4 days ago
Accounting4 days ago
 Personal Finance7 days ago
Personal Finance7 days ago
 Economics5 days ago
Economics5 days ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago