PART OF THE reason Elisha “Lishi” Baker wanted to go to Columbia University, an Ivy League university in New York, was its Middle Eastern History programme. He loved his first year and says he “felt great as a Jewish student at Columbia”. But since the Hamas attacks on Israel on October 7th, the atmosphere on campus has changed. Within days there were protests. He heard students calling for an intifada. He kept being told “you’re interpreting it wrong,” but this week there was no misinterpreting, he says, the undercurrent of antisemitism on campus.
University presidents are struggling with policing free speech on campus: specifically, how to deal with pro-Palestinian protests. After seeing timid responses by the heads of Harvard and the University of Pennsylvania lead to those presidents being forced to step down a few months ago, leaders are now trying a tougher approach. They are in danger of over-correcting.
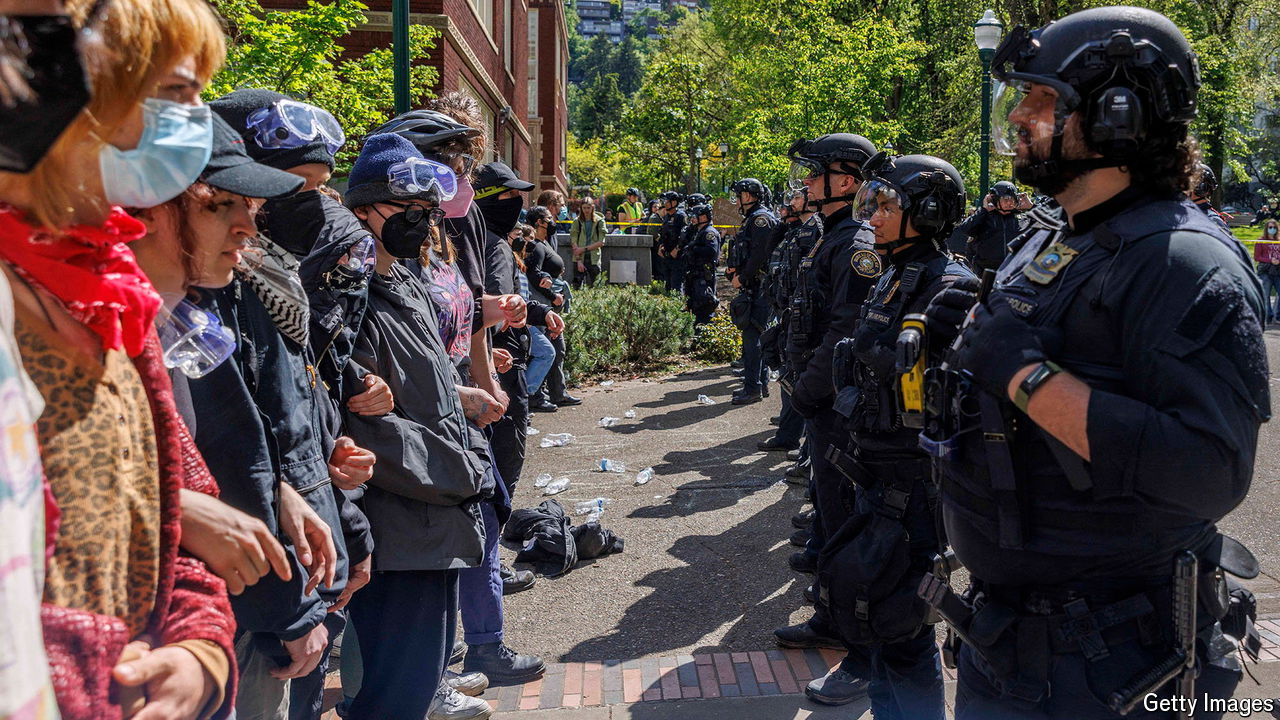
The trigger for the latest troubles was the clearing by police of tents and protesters at Columbia on April 18th, and the arrest of more than a hundred students. This was an “alarming decision”, wrote Jameel Jaffer, from the university’s semi-independent free-speech centre, adding that “it was not evident to us how the encampment and protest posed such a danger” as to justify the escalation. According to the NYPD, the arrested protesters were peaceful and offered no resistance. “It was so scary,” says Layla Saliba, who saw the arrests. “All these cops just swarming everywhere and we had people in like full riot gear.” Within days another encampment sprang up on a nearby lawn.
In a letter posted on Columbia’s website Minouche Shafik, Columbia’s president, wrote that she asked the NYPD to intervene after other efforts failed, adding that she did so “out of an abundance of concern for the safety of Columbia’s campus”. The move only inflamed matters. “The irony is that in trying to quiet things down and assert control over the encampment, the administration unleashed this firestorm,” says David Pozen, a law professor at the university.
That firestorm has now spread, with tent encampments popping up far beyond Columbia. The demands by student protesters are largely the same: divest endowments of Israeli firms and any weapons manufacturers that sell there; end academic partnerships with Israeli institutions; and condemn Israel’s actions in the war.
As at Columbia, administrators elsewhere are overcoming their reluctance to call the cops. On April 22nd nearly 50 protesters were charged with trespassing for their participation in a week-long occupation of a plaza at Yale (protesters returned the next day). At New York University police broke up a copycat encampment. Yet not all sit-ins have proved so fraught. In February a camp that had stood for four months at Stanford disbanded peacefully after administrators met students and promised more transparency on investments.
Long before the debacle at Columbia, instances of disruptive behaviour had put administrators on edge. In February pro-Palestinian activists at UC Berkeley shattered a glass door leading to a lecture by an Israeli speaker. Weeks later others interrupted an event at the home of Erwin Chemerinsky, a free-speech scholar and dean of the law school.
Last year Columbia suspended two pressure groups, Students for Justice in Palestine and Jewish Voice for Peace, for organising unauthorised demonstrations. The New York Civil Liberties Union has sued over the move. Equally controversial was the University of Southern California’s decision to cancel the graduation speech of its pro-Palestinian valedictorian, who is Muslim; the school cited safety threats. USC has since cancelled all guest speakers at commencement.
Presiding over an American university was once a plum job; now it is a minefield. On April 17th Dr Shafik was the latest one to be grilled by the House Education Committee about antisemitism on campus. Unlike the presidents of Harvard and the University of Pennsylvania, who fumbled their appearances in December, Dr Shafik survived—for now. When she and colleagues were asked the question that both Claudine Gay, at Harvard, and Elizabeth Magill, at Pennsylvania, had struggled with—whether calling for the genocide of Jews violated their university’s code of conduct—they answered simply “yes, it does.”
Critics say she did not do enough to stand up for free speech. In his letter from Columbia’s First Amendment Institute, Mr Jaffer expressed dismay. The university’s rules, he wrote, guarantee broad protection “even for speech that is objectionable or offensive to some listeners”. In her own public letter, Dr Shafik says in her defence that “we cannot have one group dictate terms and attempt to disrupt important milestones like graduation to advance their point of view.”
Dr Shafik is not out of the woods. This week she faced threats from donors to withdraw their funding and calls to resign by several politicians. On April 22nd all of New York’s Republican House members signed a letter by Elise Stefanik, a high-ranking Republican, calling for her resignation. Politicians supposedly concerned about the climate on campuses have made administrators’ jobs even more complex.
At Columbia, campus life is now disrupted for the majority of students not taking part in protests. Classes have moved online. Many professors have “walked out” in solidarity. Helicopters circle above and police in riot gear stand ready nearby. The bull-horns from protesters outside the gates are loud enough to hear across campus: students studying for MCATS, an exam for medical school, cannot find a quiet spot to take practice tests. ■

 Finance1 week ago
Finance1 week ago
 Accounting6 days ago
Accounting6 days ago
 Accounting1 week ago
Accounting1 week ago
 Stock News1 week ago
Stock News1 week ago
 Personal Finance6 days ago
Personal Finance6 days ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Finance1 week ago
Finance1 week ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago