Rising inflation in March didn’t deter consumers, who continued shopping at a more rapid pace than anticipated, the Commerce Department reported Monday.
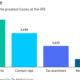
Retail sales increased 0.7% for the month, considerably faster than the Dow Jones consensus forecast for a 0.3% rise though below the upwardly revised 0.9% in February, according to Census Bureau data that is adjusted for seasonality but not for inflation.
The consumer price index increased 0.4% in March, the Labor Department reported last week in data that also was higher than the Wall Street outlook. That means consumers more than kept up with the pace of inflation, which ran at a 3.5% annual rate for the month, below the 4% retail sales increase.
Excluding auto-related receipts, retail sales jumped 1.1%, also well ahead of the estimate for a 0.5% advance. The core control group, which strips out several volatile measures and is in the formula to determine gross domestic product, also increased 1.1%
A rise in gas prices helped push the headline retail sales number higher, with sales up 2.1% on the month at service stations. However, the biggest growth area for the month was online sales, up 2.7%, while miscellaneous retailers saw an increase of 2.1%.
Multiple categories did report declines in sales for the month: Sporting goods, hobbies, musical instruments and books posted a 1.8% decrease, while clothing stores were off 1.6%, and electronics and appliances saw a 1.2% drop.
Stock market futures added to gains following the report, while Treasury yields also pushed sharply higher. The upbeat outlook for the Wall Street open came despite an escalation over the weekend in Middle East tensions as Iran launched aerial strikes on Israel. Stocks surrendered gains later in the session as yields surged.
“Strong sales growth in March salvaged an otherwise mediocre quarter for retailers,” said Jim Baird, chief investment officer at Plante Moran Financial Advisors. “Q1 growth isn’t going to generate a round of high fives, but closing out the quarter on a strong note should allow them to breathe a sigh of relief and a glimmer of hope that momentum could carry through into the coming months.”
Resilient consumer spending has helped keep the economy afloat despite higher interest rates and concerns over stubborn inflation. Consumer spending accounts for nearly 70% of U.S. economic output so it is critical to continued growth in gross domestic product.
Monday’s data comes with market concerns elevated over the path of monetary policy. Federal Reserve officials have expressed caution about cutting interest rates while inflation pressures continue, and investors have been forced to reduce their expectation for easing in policy this year.
Stronger consumer spending could cause the Fed to hold off longer on cuts, said Andrew Hunter, deputy chief U.S. economist at Capital Economics.
“Alongside the recent resurgence in employment growth, the continued resilience of consumption is another reason to suspect the Fed will wait longer before starting to cut interest rates, which now we think won’t happen until September,” Hunter said in a note after the retail sales release.
Market pricing, which has been highly volatile over the past several weeks, also is pointing to the first cut coming in September, according to the CME Group’s FedWatch gauge of futures prices.
In other economic news Monday, the Empire State Manufacturing index, which gauges activity in the New York region, increased in April from a month ago but remained in contraction territory. The index hit -14.3, better than the -20.9 reading for March but below the Dow Jones estimate for -10.
The index measures the percentage of firms reporting expansion against contraction, so anything below zero represents contraction. Shipments and delivery time readings saw a decline, while prices paid increased.

 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Accounting1 week ago
Accounting1 week ago
 Blog Post5 days ago
Blog Post5 days ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Economics6 days ago
Economics6 days ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Finance1 week ago
Finance1 week ago