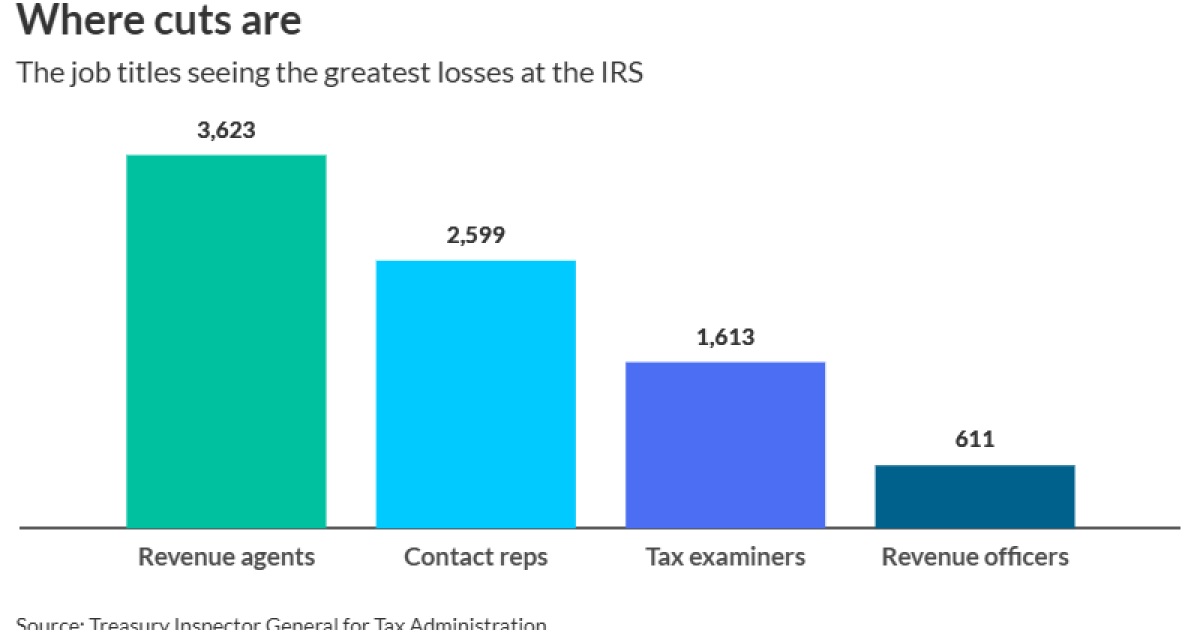
In a previous article, I discussed ways that accounting firms can learn from the technology vendors that serve them. Here, we continue exploring lessons that accountants can learn from vendors, with a focus on one of the most pressing challenges in our profession: talent management. With a massive capacity issue at hand, anything firms can do to better engage, retain and attract talent will help immeasurably.
1. Embrace a meritocracy
A lesson that accounting firms can take from tech vendors is the value of a meritocratic culture, where top talent is promoted and given opportunities to excel based on performance, not tenure or seniority. This is a core value at successful technology companies: rewarding talent based on impact.
During my time working in Google’s finance team, I had the privilege of working with leaders like Sheryl Sandberg, the former COO of Facebook, and Sukhinder Singh Cassidy, the current CEO of Xero. One thing that stood out was their ability to make objective, impact-driven decisions when it came to promotions and talent management. They prioritized the greatest contributors and those who demonstrated the highest potential for the business, regardless of how long they had been at the company.
Historically, CPA practices have been seniority-driven, which worked well when there was a steady pipeline of accountants and workplace stability. But today’s reality is different. The number of new accountants entering the profession is dwindling, and those that do have a wide range of career options that go far beyond the traditional accounting partnership model. This was abundantly clear from a panel at Botkeeper’s conference AI Unchained, where we discussed alternative structures including accounting platforms, franchises and ESOPs.
As firm leaders, you might be concerned that this approach could cause friction among long-standing team members. After all, promoting a newer team member over someone who has been around longer can ruffle feathers. However, the alternative is riskier: If your top performers aren’t recognized or given opportunities to shine, they will leave. A-players attract A-players. Creating a culture where top performers are disengaged or overlooked can lead to talent loss, which is far more damaging in the long run. By embracing a meritocratic approach, you ensure that your firm’s future is powered by those who thrive in this current reality.
2. Make cross-training a foundation of your practice
In the tech world, wearing multiple hats is the norm. When I worked at Siri (yes, the iPhone assistant, which was eventually acquired by Apple), individuals with cross-functional skills were the norm, not the exception.
Engineers didn’t just code; they also created product designs. Product managers didn’t just product manage; they also handled parts of marketing. This kind of cross-training at tech vendors didn’t just build versatility in an era where agility is needed, it also fostered collaboration and innovation.
In accounting, cross-training can be just as impactful. For example, at the Botkeeper conference panel titled “Walking a Tightrope Between Evolving Technologies and Traditional Accounting” with Angie Grissom (Rainmaker), Geni Whitehouse (ITA) and Mike Maksymiw (Aprio Alliance), the group lamented how the accounting curriculum still doesn’t teach future CPAs data literacy or interpretation skills.
Imagine an accounting firm where every accountant is cross-trained in data analytics. Not only would this prepare them for the future, but it would also allow them to deliver higher-value services to clients. Instead of being confined to compliance work, these cross-trained accountants could provide strategic insights that help clients grow their businesses.
Cross-training doesn’t just benefit the firm’s services offerings — it engages and motivates employees. When team members are given the opportunity to develop new skills and wear different hats, they feel more valued and challenged. This sense of empowerment drives higher performance and fosters loyalty. Employees who feel like they are growing and expanding their skill set are far more likely to stay with a firm long-term. Cross-training offers them a sense of progress and personal investment in their career growth, which in turn increases their commitment to the firm.
3. Use both quantitative and qualitative feedback to manage talent
Tech vendors have long been applying business performance management principles to talent management. At my company Aiwyn, we regularly conduct pulse employee engagement surveys where team members rate their satisfaction across different vectors. We gather both qualitative and quantitative feedback, ensuring that we have a clear understanding of how employees feel, where they see room for improvement, and where they feel supported.
Accounting firms can adopt a similar approach. You wouldn’t run your business without tracking financial metrics, so why run your talent management program without tracking employee satisfaction? Regular pulse surveys, engagement metrics and feedback loops give you a real-time understanding of your team’s morale. This allows you to address issues before they become problems and ensure that your employees feel valued, heard and engaged.
Implementing KPIs for talent management helps you identify trends over time. Are certain teams consistently reporting low engagement scores? Is there a department where turnover is unusually high? By analyzing the data, you can take proactive steps to improve your workplace culture and retain top talent.
In conclusion, the traditional methods of managing talent for an accounting practice no longer align with the realities of today’s workplace. By taking lessons from tech vendors, firms can adopt a more meritocratic approach, make cross-training a core part of their culture, and use data-driven insights to improve employee engagement and retention.
Do you want to build a workplace that attracts top talent and helps your team thrive in an era of rapid technological change? By embracing these modern talent management strategies, you’ll position your firm to thrive in a rapidly changing world.


 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Accounting1 week ago
Accounting1 week ago
 Blog Post5 days ago
Blog Post5 days ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Economics6 days ago
Economics6 days ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Finance1 week ago
Finance1 week ago