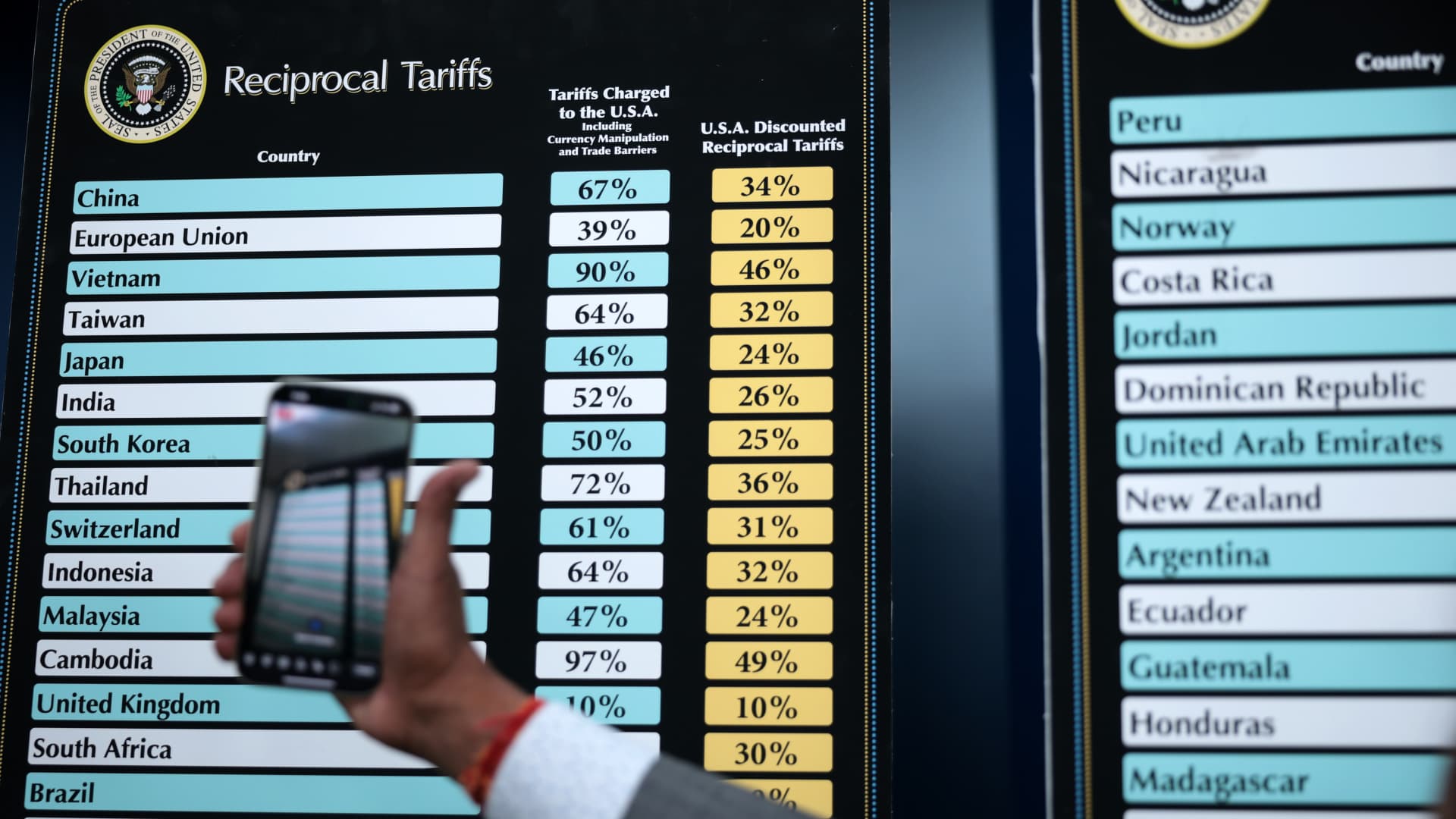
U.S. President Donald Trump on Wednesday laid out the “reciprocal tariff” rates that more than 180 countries and territories will face under his sweeping new trade policy.
The announcement sent stocks tumbling and prompted investors to seek refuge in assets perceived to be safe.
Analysts generally had a pessimistic take on the announcement, with some even predicting an increased risk of a recession for the U.S.
Here is a compilation of reactions from experts and analysts:
Tai Hui, APAC Chief Market Strategist, J.P. Morgan Asset Management
“Today’s announcement could potentially raise U.S. average tariff rates to levels not seen since the early 20th century. If these tariffs persist, they could materially impact inflation, as U.S. manufacturing struggles to ramp up capacity and supply chains pass on costs to consumers. For instance, advanced semiconductor manufacturers in Taiwan may not absorb tariff costs without viable substitutes.
“The scale of these tariffs raises concerns about growth risks. U.S. consumers may cut back on spending due to pricier imports, and businesses might delay capital expenditures amid uncertainty about the tariffs’ full impact and potential retaliation from trade partners.”
David Rosenberg, President and founder of Rosenberg Research
“There are no winners in a global trade war. And when people have to realize, when you hear this clap trap about how consumers in United States are not going to bear any brunt. It’s all going to be the foreign producer. I roll my eyes whenever I hear that, because it shows a zero understanding of how trade works, because it is the importing business that pays the tariff, not the exporting country.
And a lot of that will get transmitted into the consumer, so we’re in for several months of a very significant price shock for the American household sector.”
Anthony Raza, Head of Multi-Asset Strategy, UOB Asset Management
“They’ve come up with the most extreme numbers that we can’t even comprehend. How they’re coming up with these? And then in terms of timing, I think we were hopeful that maybe this would be something that was rolled out over the course of a year, that would allow like time for negotiations or whatever. But it does seem like the timing is much more immediate and is, again, worse than our worst-case type scenario in terms of flexibility.”
David Roche, Strategist, Quantum Strategy
“These tariffs are not transitional. They are core to President Trump’s beliefs. They mark the shift from globalisation to isolationist, nationalist policies – and not just for economics. The process will last several years and be felt for decades. There will be spillovers into multiple policy domains such as geopolitics.
Right now, expect retaliation, not negotiation by the EU (targeting U.S. services) and China (focusing on U.S. strategic and business interests). The Rose Garden tariffs will cement the bear market. They will cause global stagflation as well as U.S. and EU recession.”
Shane Oliver, Head of Investment Strategy and Chief Economist, AMP
“Our rough calculation is that the 2nd April announcement will take the US average tariff rate to above levels seen in the 1930s after the Smoot/Hawley tariffs which will in turn add to the risk of a US recession – via a further blow to confidence and supply chain disruptions – and a bigger hit to global growth.
“The risk of a US recession is probably now around 40% and global growth could be pushed towards 2% (from around 3% currently) depending on how significant retaliation is and how countries like China respond with policy stimulus.”
Tom Kenny, Senior International Economist, ANZ
“Today’s announced US reciprocal tariffs are worse than expected. The effective tariff rate on U.S. merchandise imports is likely to climb to the 20-25% range, the highest since the early 1900s.
Yields on inflation-indexed bonds were higher and equities sold off after the announcement, suggesting the market thinks these tariffs will hurt growth and add to inflation. Market pricing of the federal funds rate points to cuts from the Federal Reserve coming sooner.”

 Blog Post6 days ago
Blog Post6 days ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Accounting1 week ago
Accounting1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Accounting1 week ago
Accounting1 week ago
 Finance1 week ago
Finance1 week ago