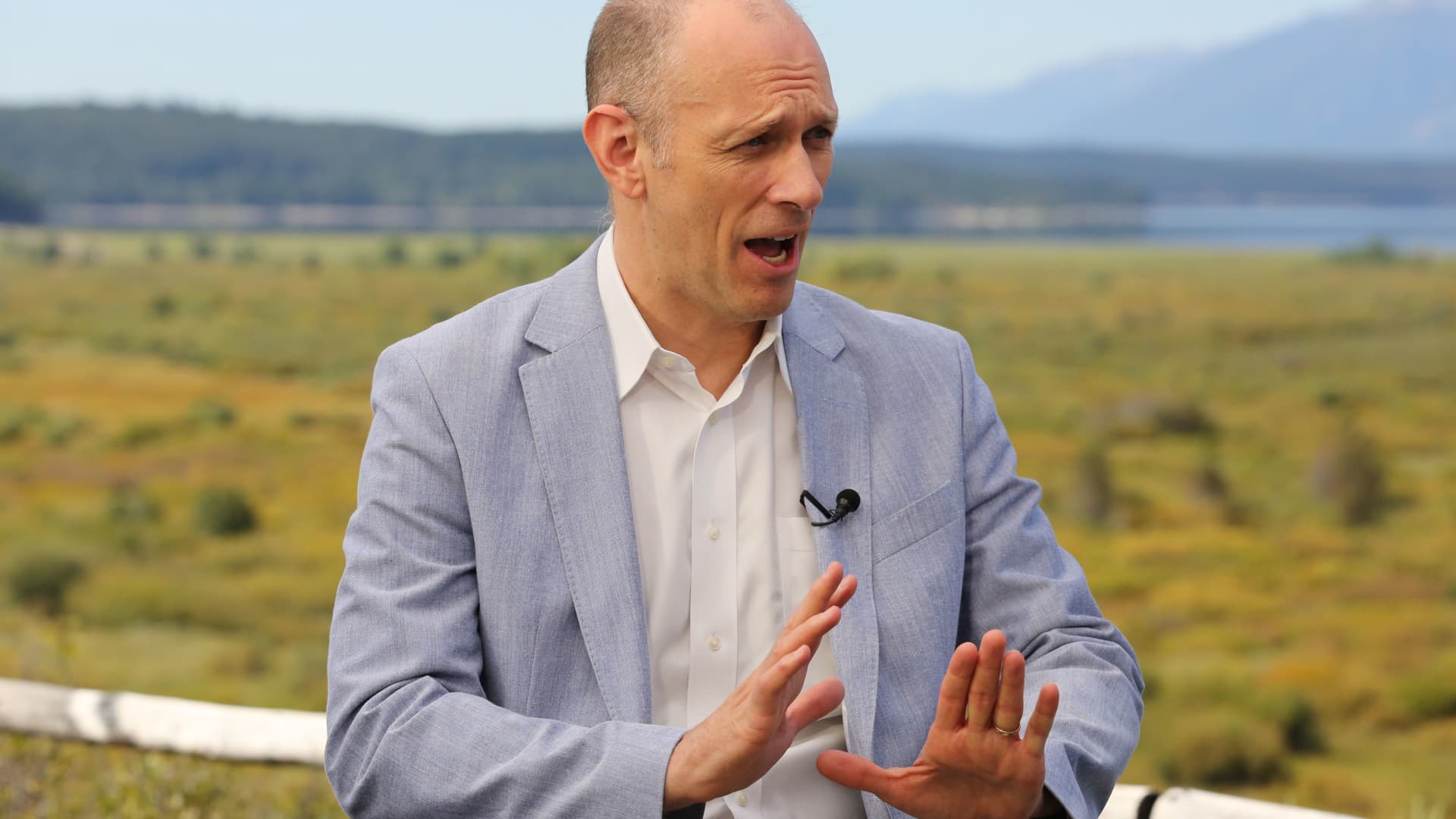
Chicago Federal Reserve President Austan Goolsbee on Monday vowed that the central bank would react to signs of weakness in the economy and indicated that interest rates could be too restrictive now.
Asked whether weakening in the labor market and manufacturing sector could prompt a response from the Fed, Goolsbee did not commit to a specific course of action but said it does not make sense to keep a “restrictive” policy stance if the economy is weakening. He also declined to comment on whether the Fed would institute an emergency intermeeting cut.
“The Fed’s job is very straightforward: maximize employment, stabilize prices and maintain financial stability. That’s what we’re going to do,” the central bank official said during an interview on CNBC’s “Squawk Box” program. “We’re forward-looking about it. So if the conditions collectively start coming in like that on the through line, there’s deterioration on any of those parts, we’re going to fix it.”
The interview occurred with markets in turmoil.
Futures tied to the Dow Jones Industrial Average were off nearly 1,300 points, or close to 3%, as Treasury yields plummeted. The moves continued a downward trajectory that began Thursday, a day after the Fed opted not to lower interest rates, raising concerns that policymakers were behind the curve as inflation falls and the economy weakens.
Those fears were heightened Friday when the Labor Department said nonfarm payrolls increased by just 114,000 and the unemployment rate climbed to 4.3%, triggering a signal known as the Sahm Rule that the economy could be in recession.
However, Goolsbee said he does not believe that to be the case.
“Jobs numbers came in weaker than expected, but [are] not looking yet like recession,” he said. “I do think you want to be forward-looking of where the economy is headed for making the decisions.”
He also said, however, that Fed policy is restrictive now, a position it should only be in if the economy looks like it is overheating. The central bank has kept its benchmark rate in a range between 5.25% and 5.5% since July 2023, the highest level in some 23 years.
“Should we reduce restrictiveness? I’m not going to bind our hands of what should happen going forward because we’re still going to get more information. But if we are not overheating, we should not be tightening or restrictive in real terms,” he said.
Policymakers have been focused on the “real” fed funds rate, which is the Fed’s benchmark minus the inflation rate. As inflation declines, the real rate increases — unless the Fed chooses to cut. The real rate now is around 2.73%. Fed officials judge the long-term real rate to be closer to 0.5%.
Markets expect the Fed to head into an aggressive easing mode, starting in September with a 0.5 percentage-point rate cut that is now fully priced in as measured by 30-day fed funds futures contracts. Traders expect the Fed to slice 1.25 to 1.5 percentage points off the funds rate by the end of the year, according to the CME Group’s FedWatch Tool.

 Blog Post1 week ago
Blog Post1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Finance1 week ago
Finance1 week ago
 Accounting1 week ago
Accounting1 week ago
 Personal Finance7 days ago
Personal Finance7 days ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Finance1 week ago
Finance1 week ago