High-rise buildings are illuminated at night in the West Coast New Area of Qingdao, East China’s Shandong province, on March 22, 2024.
Nurphoto | Nurphoto | Getty Images
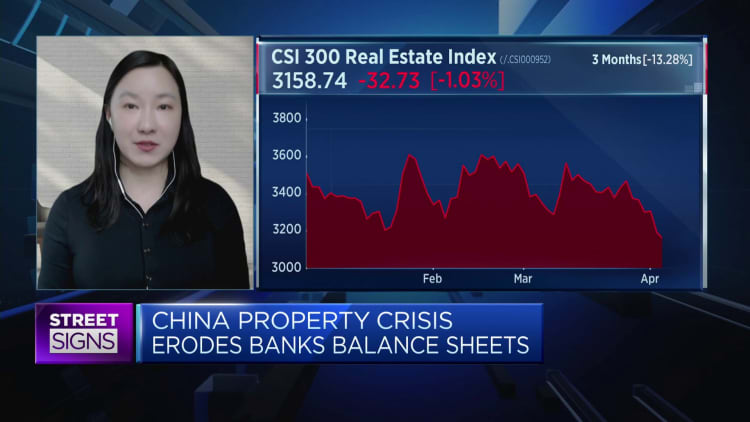
BEIJING — China’s real estate troubles are likely far from over and industry problems need to be addressed quickly if overall GDP growth is to pick up significantly, according to a report released Thursday by global investment firm KKR.
That’s one of the two key takeaways from a recent trip to China by the firm’s head of global and macro asset allocation, Henry H. McVey. It was his fourth visit in just over a year.
“A fundamentally overbuilt real estate industry needs to be addressed — and quickly,” he said in the report, which counts Changchun Hua, KKR’s chief economist for Greater China, among the co-authors.
“Second, confidence must be restored to drive savings back down,” McVey said, noting that would spur consumers and businesses to spend on upgrading to higher quality products, as Chinese authorities have promoted.
Real estate and related sectors once accounted for about one fifth or more of China’s economy, depending on the breadth of analysts’ calculations. The property industry has slumped in the last few years after Beijing’s crackdown on developers’ high reliance on debt for growth.
Based on comparisons to housing corrections in the U.S., Japan and Spain, China’s “housing market correction may be just halfway complete” in terms of its depth, the KKR report said.
“Both price and volume must come under pressure to finish the cleansing cycle,” the report said. “To date, though, it has largely been a contraction in volume.”
While KKR’s report didn’t provide much detail on expectations for specific real estate policy, the authors said more action by Beijing to improve China’s real estate sector “could materially shift investor perception.”
Amid geopolitical tensions, the country’s property market slump and drop in stocks have given many foreign institutional investors pause about China investing.
“According to some of our proprietary survey work, many allocators have considered reducing China exposure to 5-6%, down from 10-12% today at a time that we think fundamentals in the economy are likely bottoming,” the KKR report said.
Much of official Chinese data to start the year beat analysts’ expectations.
Chinese officials have said the real estate sector remains in a period of adjustment, while Beijing shifts its emphasis toward manufacturing and what it considers “high-quality development.”
Authorities have also released policies to promote financial support for select property developers, while many local governments — though not necessarily the largest cities — have significantly relaxed home purchase restrictions.
Real estate’s drag to moderate
KKR expects a modest slowdown in China’s GDP growth to 4.7% this year, and 4.5% next year, with real estate and Covid-related factors halving their drag on the economy from 1.4 percentage points in 2024 to a 0.7 percentage point drag in 2025.
“Our bottom line is that: with the ongoing [property] correction as well as some potential further policy support, we think the drag to [the] overall economy should moderate a bit over the next few years,” McVey said in a separate statement. He is also chief investment officer of KKR Balance Sheet.
Catering, accommodation and wholesale are set to modestly increase their contribution to growth in the next two years, while digitalization and the shift toward more carbon-neutral, green industry are expected to remain the largest drivers of growth, according to the report.
For investors, the report said a more important development than China’s GDP increase would be whether authorities could make it easier for businesses and households to tap capital markets.
“Repairing soft spots in [the] economy, especially around housing, will ultimately improve the cost of capital, and will also allow new consumer companies to access the capital markets likely at better prices if real estate and confidence are doing better,” McVey said in the statement.
Beijing in March announced a GDP target of around 5% for this year. Minister of Housing and Urban-Rural Development Ni Hong said last month that developers should go bankrupt if necessary and that authorities would promote the development of affordable housing.
Recent data have pointed to some stabilization in the property sector slowdown. The seven-day-moving average of new home sales in 21 major cities fell by 34.5% year-on-year as of Monday, better than the 45.3% drop recorded a week earlier, according to Nomura, citing Wind Information.
Compared with the same period in 2019, that sales average was only down by 27.8% as of Monday, versus a 47% drop a week earlier, Nomura said, noting most of the improvement was in China’s biggest cities.
Consumer outlook
KKR said most of its local portfolio is in consumer and services companies, whose business reflect how Chinese people in the middle to higher income range are spending modestly to upgrade their lifestyles.
“Top line growth is solid, margins are holding, and consumers are spending on less conspicuous items such as ‘smart homes,’ pets, and recreational activities,” the report said. “Domestic travel is also strong.”
Retail sales rose by a better-than-expected 5.5% year-on-year in January and February, boosted by significant growth in Lunar New Year holiday spending.
Longer term, KKR still expects that China can follow historical precedent in changing policy to be “more investor friendly.”
“While our message is not an all-clear signal to lean in,” the report said, “it is a reminder – using history as our guide – that, if China does adjust its domestic policies to be more investor friendly (especially as it relates to supply side reforms), this market could rebound significantly from current levels.”

 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week ago
 Economics5 days ago
Economics5 days ago
 Accounting5 days ago
Accounting5 days ago
 Economics4 days ago
Economics4 days ago
 Economics5 days ago
Economics5 days ago
 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week ago
 Economics6 days ago
Economics6 days ago