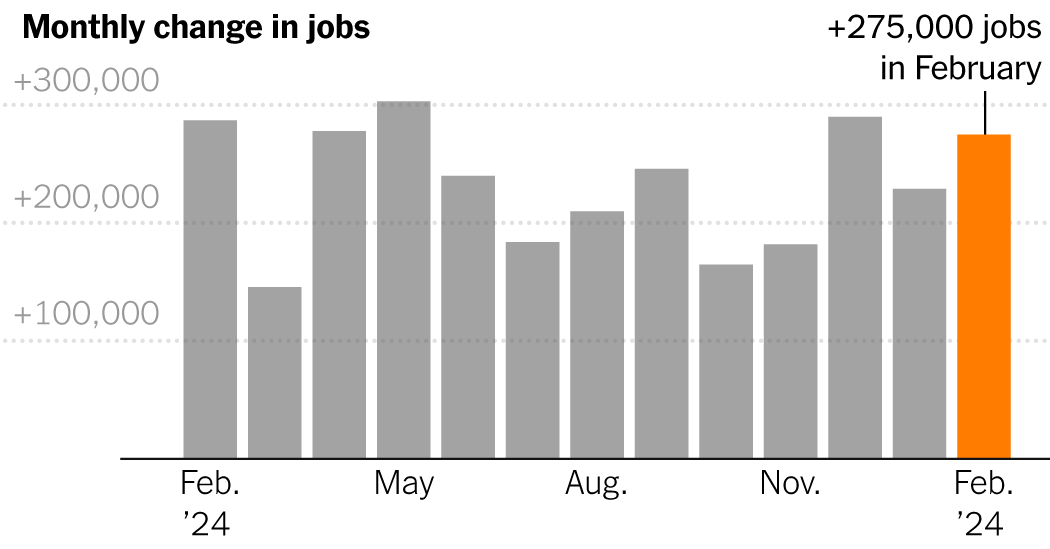Economics
U.S. Employers Add 275,000 Jobs in Another Strong Month
-

 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week agoHow appealing property taxes can benefit new homeowners
-

 Blog Post1 week ago
Blog Post1 week agoHow to Implement Internal Controls to Prevent Business Fraud
-

 Economics6 days ago
Economics6 days agoElon Musk says Trump’s spending bill undermines the work DOGE has been doing
-

 Economics1 week ago
Economics1 week agoMAGA: protecting the homeland from Canadian bookworms
-

 Accounting6 days ago
Accounting6 days agoHighest paid jobs in corporate accounting
-

 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week agoHow to pay college tuition bills with your 529 plan
-

 Economics6 days ago
Economics6 days agoHow young voters helped to put Trump in the White House
-

 Personal Finance6 days ago
Personal Finance6 days agoHarvard, Trump international enrollment battle affects college applicants